Structure of Muscles - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Structure of Muscles
Description:
Isometric: (static) exercises in which muscles contract, but the body parts do ... Body Building: sport can also be done for competition, athletes are primarily ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:47
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Structure of Muscles
1
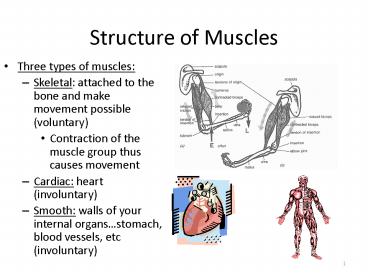
Structure of Muscles
- Three types of muscles
- Skeletal attached to the bone and make movement
possible (voluntary) - Contraction of the muscle group thus causes
movement - Cardiac heart (involuntary)
- Smooth walls of your internal organsstomach,
blood vessels, etc (involuntary)
2
Strength Building Exercises
- Isometric (static) exercises in which muscles
contract, but the body parts do not move (ex
pressing against a wall) - Isotonic (dynamic) exercises in which the
muscles contract and so do the body parts (ex
leg curl, push-up, curl-up, lat-pull, etc.) - Isokinetic exercises done with a special
apparatus that control the speed of the movement
of a body part so that it remains constant, even
when you try to move faster (for rehabilitation
purposes)
3
Muscle Fibers
- Muscle fibers are muscle cells, which are long,
thin, and cylinder-shaped - The strength and endurance of skeletal muscle
depends on whether the muscles are made of slow,
fast, or intermediate fibers and how much
exercise they get - Slow-twitch contract at a slow rate and have
good endurance - Fast-twitch contract at a fast rate and used for
strength activities - Intermediate have characteristics of both slow
and fast-twitch (endurance and strength) - The types of fibers in our muscles are determined
by our genes however, we can increase the
strength and endurance of our muscles by proper
training
4
Different Forms of Weight Training
- Weight Training non-competitive form of exercise
done to increase strength and endurance - Resistance Training involves the lifting of
weights to build strength and endurance
w/machines (safer) - Circuit Weight Training same as weight training
except it is usually done to develop aerobic
training as well as strength and muscular
endurance - Weight Lifting Olympic sport involving the use
of free weights. Athletes attempt to lift a
maximum load (the snatch and the clean and jerk) - Power Lifting competitive sport using free
weights, athletes attempt to lift a maximum load
(squat, bench press and deadlift) - Body Building sport can also be done for
competition, athletes are primarily concerned
about how large and well-defined their muscles are
5
Muscle Fitness Assessment
- One Repetition Maximum (1RM)
- The amount of weight/resistance that can be
overcome in one repetition - considered to be the best test for muscular
strength - Ex Bench press, Leg press, Vertical Leap, etc
- Calisthenics
- Exercises done using all or part of your body
weight for resistance - Typically used for muscular endurance
self-assessment - Ex Curl-ups, Push-ups, etc.
6
Absolute Versus Relative Strength
- Absolute Strength
- Measured by how much weigh or resistance you can
overcome regardless of your body size - Relative Strength
- Strength adjusted for your size
- Can be found dividing your strength by your body
weight to give you an estimate
7
Health and Wellness Benefits
- Strength the amount of force a muscle exerts
- Health and Wellness Benefits
- Helps you jump and lift
- Helps you work and play with less fatigue
- Prevents muscle injuries and soreness
- Muscles burn more calories than fat does
- Helps maintain good posture
8
Myths and Misconceptions
- No pain, no gain!
- FALSE! Pain is your bodies way of telling you it
is hurting. - Body Dysmorphia
- Term used when people become obsessed about with
building muscle - Obsessive-compulsive disorder, and can be very
dangerous - Some people think that only males need to be
concerned about their strength - FALSE!...both males and females need strength to
be healthy, to avoid injury, to look good, and to
be able to help themselves or others in an
emergency - Some women fear that strength training will cause
their bodies to look masculine - Falsehormones in womens bodies prevent them
from developing large bulky muscles - Both men and women look more attractive with
strong muscles because they are more likely to
have good posture and firm bodies
9
Fitness Principles and Strength
- Overload increase the load so that the muscle
can contract harder than normal - Progression gradually increase resistance
- Specificity specifically overload the muscles
you want to strengthen and do exercises that
closely resemble the movement that you want to
use - Principle of Rest and Recovery you need to allow
your muscles to recover after training (about 48
hours to rebuild)
10
Resistance Training Guidelines
- Do not hold your breath when you lift
- Always be sure to use spotters when working with
free weights - Avoid maximal lifts, start with a moderate
program - Avoid overhead lifts with free weights (use
machines instead) - Learn proper form, avoid positions that cause
your lower back to bend wrong or your wrists to
bend backwards - Avoid plyometrics until you are old enough (power
moves too) - Never use weights carelessly
- Concentrate on your technique and what youre
doing
11
Resistance Training Guidelines Continued
- Use resistance that you can lift 7-10 reps, your
muscles may be able to lift more, but your bones
are not - Do not compete when lifting weights, genetic
differences largely determine how strong a person
can be - Consider other forms of resistance such as
calisthenics, elastic bands, or isometrics - Do not try to become muscle-bound to have
tight, bulky muscles that prevent individuals
from moving freely, it is not strength training,
but rather incorrect strength training
(neglecting muscle groups)