Endergonic vs' exergonic reactions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Endergonic vs' exergonic reactions
Description:
Relationship between the equilibrium constant and concentration ... Noncompetitive inhibitor. binds to a different site. and induces a change at. the active site ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:84
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Endergonic vs' exergonic reactions
1
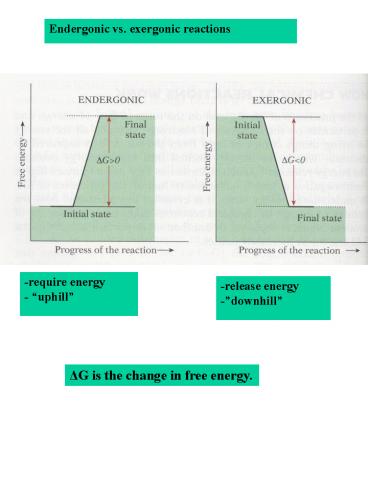
Endergonic vs. exergonic reactions
-require energy - uphill
-release energy -downhill
?G is the change in free energy.
2
?G is the change in free energy.
Keq product concentration reactant
concentration
3
Relationship between the equilibrium constant and
concentration
The equilibrium constant (final ratio of products
to reactants), is independent of the starting
concentrations.
4
Energy changes in an exergonic reaction
Ea is the activation energy.
5
Action of platinum as a catalyst
- Pt forms weak temporary bonds with molecules of
hydrogen (blue) - and oxygen (red).
- This binding draws hydrogen and oxygen electrons
from their covalent - positions (and weakens bonds within their
respective molecules). - 3. Also, the spacing of the Pt atoms tends
to align hydrogen and oxygen so - that new hydrogen-oxygen bonds form more easily.
6
Reduction of activation energy by catalysts
7
Effect of a catalyst on the ability of kinetic
energy to activate a reaction
Catalysts lower the energy necessary for the
reaction so that more reactants can combine to
form products
8
Enzyme activity and temperature
Enzyme activity rises with temperature until
thermal denaturation causes a sharp decline.
9
Enzymes are sensitive to pH
Most enzymes are very sensitive to pH, but they
differ in the pH values at which they are most
active.
10
Induced-fit model of enzyme-substrate interaction
Enzyme has an active site
Enzyme-substrate complex forms binding causes
conformational change
Enzyme changes back when product is released
11
Active site of an enzyme
Many enzymes have prosthetic groups (here, zinc)
that are essential to activity.
12
Inhibition of an enzyme
Enzyme-substrate complex
Competitive inhibitor binds to the active site
Noncompetitive inhibitor binds to a different
site and induces a change at the active site