Astronomy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
Astronomy
Description:
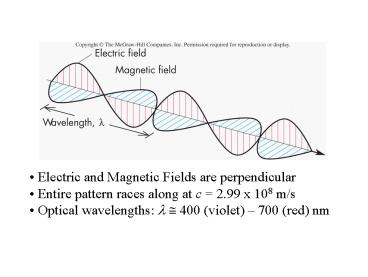
... are perpendicular. Entire pattern races along at c = 2.99 x 108 m/s ... RAY - 'geometrical optics' reflection and refraction in mirrors, lenses, telescopes ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:20
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Astronomy
1
- Electric and Magnetic Fields are perpendicular
- Entire pattern races along at c 2.99 x 108 m/s
- Optical wavelengths l ? 400 (violet) 700
(red) nm
2
The REAL rainbow
3
Four Ways of Thinking about EM radiation
- RAY - geometrical optics reflection and
refraction in mirrors, lenses, telescopes - WAVE - diffraction optics interference and
diffraction, amounts reflected, transmitted - from VIS, to IR, to radio
- PHOTON - absorption and emission spectra of hot
gases from VIS, to UV, to x-ray, to g-ray - PHOTON GAS - diffusion, cosmic background
4
The atmosphere is mostly opaque except in the
visible, some IR and radio
The Doppler Effect works for light too
- if object moves AWAY viewer light is
red-shifted - if object moves TOWARD viewer light is
blue-shifted - speed must be pretty large to see significant
shift - Dl/l vo/c is the formula (we wont use it)
5
The Photon Idea
- Einsteins conception in 1905
- Think of EM radiation as a PARTICLE, not a wave
- Absorbed, Emitted All at Once
- Packet of Energy E hf
- E energy in electron-volts (eV)
- f frequency in Hz
- h Plancks constant 4.14 x 10-15 eV/Hz
- Optical E ? 1.5 eV 2.5 eV (LEDs)
- Typical chemical energy
6
Energy, Power, Flux and All That
- Energy the total amount present, like a candy
bar (units Joules or eV electron-Volts) - Power the time rate at which energy is
consumed, or produced P E/t (units J/s
Watts), like a light bulb - Flux the power divided by the area over which
it is smeared F P/A (units W/m2) - Note book is goofy on this point
- If power is emitted in all directions equally
(like a star), then the flux drops off with
distance d like 1/d2 inverse-square law
7
Power emitted from a point-like source spreads
over larger and larger areas
8
Law of Reflection
Angle of Incidence Angle of Reflection
9
Law of Refraction
Rays bend toward (away) from the normal as they
pass from one medium to a more (less) optically
dense medium
10
Fig.06.18
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
For a telescope on the moon
15
Fig.06.23
CCD detectors and x-ray optics
16
How the Eye Sees the diverging cone of rays
- Two cones here one from top, one from bottom
- Image is REAL (there IS light there) and
INVERTED
17
The object is so close to the lens that a
magnified VIRTUAL (there is no light there) image
is formed Looks diverging
MORAL Convex lenses are not always converging
The object is sufficiently far from the lens that
a shrunken REAL (there is light there) image is
formed Looks converging
18
How a telescope ANGULARLY MAGNIFIES