EXAMPLE While LOOP PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: EXAMPLE While LOOP
1
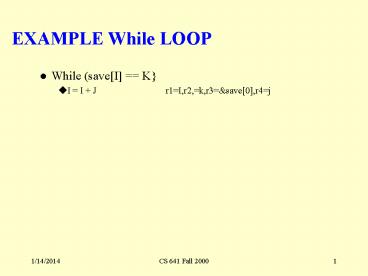
EXAMPLE While LOOP
- While (saveI K
- I I J
r1I,r2,k,r3save0,r4j
2
Integer constants
- Add r1,r2,r3
- Addi r1,r2,const (16 bits for constant)
3
How about larger constants?
- We'd like to be able to load a 32 bit constant
into a register - Must use two instructions, new "load high
immediate" instruction - lhi r1, 1010101010101010Then must get the lower
order bits right, i.e., ori r1, r1,
1010101010101010
1010101010101010
0000000000000000
0000000000000000
1010101010101010
ori
4
Call
- Load r4, first arg (some arguments in registers)
- Load r5, second arg
- Store some registers (not caller preserved)
- Jal xxxx
- Reload some registers
- XXX store other registers (callee preserved)
- Reload saved registers
- JR r31
5
Other Issues
- Things we are not going to cover linkers,
loaders, memory layout stacks, frames,
recursion manipulating strings and
pointers interrupts and exceptions system calls
and conventions - We've focused on architectural issues
6
Alternative Architectures
- Design alternative
- provide more powerful operations
- goal is to reduce number of instructions executed
- danger is a slower cycle time and/or a higher CPI
- Sometimes referred to as RISC vs. CISC
- virtually all new instruction sets since 1982
have been RISC - VAX minimize code size, make assembly language
easy instructions from 1 to 54 bytes long!
7
Evolution of Instruction Sets
Single Accumulator (EDSAC 1950)
Accumulator Index Registers
(Manchester Mark I, IBM 700 series 1953)
Separation of Programming Model from
Implementation
High-level Language Based
Concept of a Family
(B5000 1963)
(IBM 360 1964)
General Purpose Register Machines
Complex Instruction Sets
Load/Store Architecture
(CDC 6600, Cray 1 1963-76)
(Vax, Intel 432 1977-80)
RISC
(Mips,Sparc,HP-PA,IBM RS6000, . . .1987)
8
A "Typical" RISC
- 32-bit fixed format instruction (3 formats)
- 32 32-bit GPR (R0 contains zero, DP take pair)
- 3-address, reg-reg arithmetic instruction
- Single address mode for load/store base
displacement - no indirection
- Simple branch conditions
- Delayed branch
see SPARC, MIPS, HP PA-Risc, DEC Alpha, IBM
PowerPC, CDC 6600, CDC 7600, Cray-1,
Cray-2, Cray-3
9
A dominant architecture 80x86
- See your textbook for a more detailed description
- Complexity
- Instructions from 1 to 17 bytes long
- one operand must act as both a source and
destination - one operand can come from memory
- complex addressing modes e.g., base or scaled
index with 8 or 32 bit displacement - Saving grace
- the most frequently used instructions are not too
difficult to build - compilers avoid the portions of the architecture
that are slow - what the 80x86 lacks in style is made up in
quantity, making it beautiful from the right
perspective
10
80x86
- 1978 The Intel 8086 is announced (16 bit
architecture) - 1980 The 8087 floating point coprocessor is
added - 1982 The 80286 increases address space to 24
bits, instructions - 1985 The 80386 extends to 32 bits, new
addressing modes - 1989-1995 The 80486, Pentium, Pentium Pro add a
few instructions (mostly designed for higher
performance) - 1997 MMX is addedThis history illustrates
the impact of the golden handcuffs of
compatibility
11
Instruction Set Architecture
- Consider the RISC/CISC approaches
- DLX RISC example
- Intel x86 family as a CISC example
- What constitutes a good architecture?
- Consistency or doing similar things in a similar
way - Regularity or architectural features applied in a
consistent fashion - Completeness or having features that are
necessary - Parsimony or not having more than the necessary
features - Orthogonality or features sets are independent of
one-another - Transparency or low level functions do not affect
higher-level ones - Open-endedness or being expandable
12
Alternative Architectures
?1998 Morgan Kaufmann Publishers
- Design alternatives
- How to provide more powerful operations
- Improve performance by reducing number of
instructions executed - The danger is a slower cycle time and/or a higher
CPI - This alternatives become apparent when
considering RISC vs. CISC architectures - Virtually all new instruction sets since 1982
have been RISC - Counter example the VAX
- Minimized code size, make assembly language easy,
complex instructions from 1 to 54 bytes long! - We will consider several alternatives