Operational Amplifier PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Operational Amplifier
1
Operational Amplifier
2
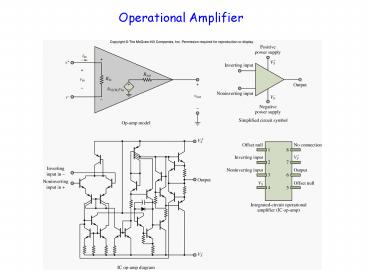
Ideal OP Amp
Circuit model
Two golden rules to perform calculations on op
amps with negative feedback
- iin0, no current flow into op amp.
- VV-
- Typically one end of op amp is connected to
ground, therefore, VV- 0V, virtual ground.
Often V is connected to ground to avoid
stability problem.
3
Applications building block for analog systems
- Amplifiers
- Adders and Substractors
- Integrators Differentiators
- Clock generators
- Filters
- Digital-to-analog converters
4
Using op-amps
No flexibility
5
Lets build a circuitnoninverting amplifier
6
When A is very large
Suppose A106, R19R, R2R
- Gain
- determined by resistance ratio
- insensitive to A, temperature, fab variation
7
Why did this happen? Negative feedback
e.g. vIN5V Suppose I perturb the circuit (e.g.
force v0 momentarily to 12V somehow Stable point
is when v?v- Key negative feedback ? portion
of output fed to ve input. e.g. Car antilock
brakes ? small corrections
8
How to control a high-strung device
- Antilock brakes
9
More op amp insights
- Observe, under negative feedback,
- We also know
- i ? 0
- i- ? 0
- ? Yield an easier analysis method (under negative
feedback)
10
Insightful analysis method under negative
feedback
11
Voltage follower
Why is this circuit useful?
has minimum effects on previous and next circuit.
12
Inverting Amplifier
Feedback resistor, always to negative input
13
Summing Amplifier Add Circuit
If RS1RS2RSNRS
14
Non-innverting Amplifier
Feedback resistor, always to negative input
15
Differential Amplifier Substractor
Very useful if both signals are corrupted with
noise Electrocardiogram (EKG)
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.