Physics 121 Lecture Summaries - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title:
Physics 121 Lecture Summaries
Description:
Gauss s Law Lecture 4 Electrostatic Potential Lecture 5 Capacitance Lecture 6 Resistance and Resistivity, Circuits Part 1 Lecture 7 DC Circuits, Part 2 – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:112
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Physics 121 Lecture Summaries
1
Physics 121 Lecture Summaries
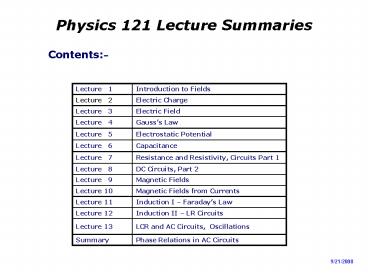
- Contents
Lecture 1 Introduction to Fields
Lecture 2 Electric Charge
Lecture 3 Electric Field
Lecture 4 Gausss Law
Lecture 5 Electrostatic Potential
Lecture 6 Capacitance
Lecture 7 Resistance and Resistivity, Circuits Part 1
Lecture 8 DC Circuits, Part 2
Lecture 9 Magnetic Fields
Lecture 10 Magnetic Fields from Currents
Lecture 11 Induction I Faradays Law
Lecture 12 Induction II LR Circuits
Lecture 13 LCR and AC Circuits, Oscillations
Summary Phase Relations in AC Circuits
9/21/2008
2
Summary Electric Charge
Lecture 2
3
Summary Electric Field
Lecture 3
4
Lecture 4
Summary Gausss Law
5
Summary Electric Potential
Lecture 5
6
Summary Capacitance
Lecture 6
7
Summary Lecture 7 - Resistance and
Resistivity
8
Summary Lecture 7 Resistive Circuits
- An emf device does work on charges to maintain a
potential difference between its output
terminals. - Kirchhoffs rules
- Loop rule. The algebraic sum of the changes
in potential encountered in a complete traversal
of any loop of a circuit must be zero. - Junction rule. The sum of the current
entering any junction must be equal to the sum of
the currents leaving that junction. - Series resistances when resistances are in
series, they have the same current. The
equivalent resistance that can replace a series
combination of resistance is - Parallel resistance when resistances are in
parallel, they have the same potential
difference. The equivalent resistance that can
replace a parallel combination of resistance is, - Single loop circuits the current in a single
loop circuit is given by - Power when a real battery of emf and internal
resistance r does work on the charges in a
current I through the battery,
9
Summary Lecture 7/8A - Circuits, Part 1
10
Summary Lecture 8B RC Circuits, Part 2
11
Summary Lecture 9 Magnetic Fields
12
Summary Lecture 10 Magnetic Fields from
Currents
13
Summary Lecture 11 Induction I Faradays Law
14
Summary Lecture 12 Induction II LR Circuits
15
Summary Lecture 13/14 - LCR AC Circuits,
Oscillations
16
Summary Phase Relations in AC Circuits