Antigen Processing and Presentation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Antigen Processing and Presentation
Description:
Antigen Processing and Presentation Cytosolic (endogenous) pathway Endocytic (exogenous) pathway Ag processing: degradation of proteins into peptides – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:53
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Antigen Processing and Presentation
1
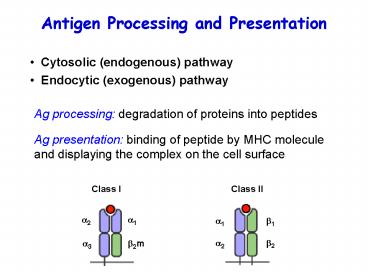
Antigen Processing and Presentation
- Cytosolic (endogenous) pathway
- Endocytic (exogenous) pathway
Ag processing degradation of proteins into
peptides
Ag presentation binding of peptide by MHC
molecule and displaying the complex on the cell
surface
2
(No Transcript)
3
Two compartments of the cell
Cytosol continuous with nucleus Vesicular
system (ER, golgi, endosomes, lysosomes)
continuous with extracellular fluid
Extracellular pathogens Endocytic
vesicles (exogenous) Class II CD4 T cells
4
(No Transcript)
5
Cytosolic pathway
- Site of peptide generation
- Site of membrane protein synthesis
- Transport of peptides into ER
- Loading of peptide onto nascent class I molecules
in ER - Display the complex on the cell surface
6
Cytosolic pathway
7
Pathogen exploitation
Plasma membrane
nucleus
ER
Golgi
vesicle
- Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV)
- US2 and US11 bind and remove nascent class I a
chain from ER
8
(No Transcript)
9
Endocytic pathway
- Site of peptide generation
- Site of MHC class II synthesis
- Loading of peptide into class II molecules
- Surface expression
Plasma membrane
10
Endocytic pathway
11
Influenza A Virus
- Segmented RNA virus
- 8 RNAs
- 10 proteins
- 15 HA
- 8 NA
- H5N1
12
(No Transcript)
13
HA and NA are highly variable
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
Interferons inhibit protein synthesis and
therefore virus replication
17
Role of T and B cells in responses to influenza
virus infection
CD8 CD4 B Clearance (days) Survival
7-10 100
- 10-14 100
- 10-14 90
- 10-14 35-85
- - gt20 0
- - gt20 0
- - gt14 20
- - - gt20 0
18
Host-Influenza Virus Interaction Host Influenz
a virus 5 triphosphate 5 cap TLR7,
RIG-I dsRNA, NS1 APOBEC NK
cells Antibody HA and NA (antigenic
shift) CTL Epitope change (antigenic drift)
19
- Principles of adaptive immunity
- TCR recognition
- Antigen presentation and processing
- Host defense against viruses