Chapter 9 Joints - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 46
Title:
Chapter 9 Joints
Description:
Title: Joint Classification Author: IT SPD Last modified by: Learning Resource Center Created Date: 12/7/1999 3:06:02 AM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:127
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 9 Joints
1
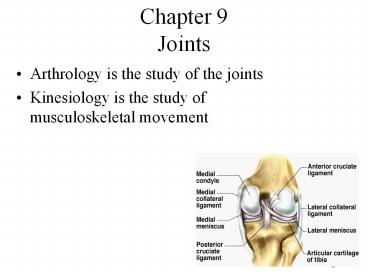
Chapter 9Joints
- Arthrology is the study of the joints
- Kinesiology is the study of musculoskeletal
movement
2
2 CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS
- 1. How the bones are joined
- fibrous, cartilaginous, bony and synovial joints
- 2. How the bones move
- We will look at this type of joint mainly
3
Three types of Joint MOVEMENT
- Three ways bones move
- 1. Freely
- 2. Slightly
- 3. Not at all
- A freely moving joint is a DIARTHROSES
- This includes All synovial joints
- Slightly moving is a AMPHIARTHROSIS
- No movement is a SYNARTHROSIS
4
SYNARTHROSIS
- Synarthrosis ( How much does this move?), three
types - 1. Suture
- 2. Gomphosis
- Teeth
- 3. Synchondroses (SYN together, chrondro
cartilage - Epiphyseal plate
5
AMPHIARTHROSIS
- Amphiarthrosis (moves ________), two types
- 1. Syndesmosis (struck rock twice)
- Distal tibiofibular joint
- (picture tibula and fibula stricking each other)
- 2. Symphyses
- Always in the midline of the body
- Pubic symphyses
- Intervertebral disc
6
Making Sense of JointsCartilage becomes Bone
- A Synchondrosis 2 bones, once separate, fused by
osseous tissue - An example is the epiphyseal plate at the end of
growing bones - As the bone grows the synchondrosis (cartilage)
is replaced by bone and becomes a synostosis
(ost- is bone)
7
Synarthrosis Joints(Immovable Joint)
- Synathrosis
- Fibrous joints of collagen fibers in space
between bones - sutures, synchondroses, synostosis, gomphosis
8
Amphiarthrosis(Slightly Moveable Joint)
- Symphysis
- pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs
- Syndesmosis
- Distal tibia and fibula joint
9
Diarthrosis (Freely Moveable) I
- Space between bones called the synovial (joint)
cavity - Contains articular capsule and an articular
cartilage - 1. Articular capsule is composed of two layers
- 1) the outer fibrous capsule
- lined by synovial membrane
- continuous with periosteum
- 2) the inner synovial membrane
- a) which secretes a lubricating and
joint-nourishing synovial fluid - viscous slippery fluid rich in albumin
similar to raw egg white - 2. Articular cartilage
- hyaline cartilage covering the joint surfaces
10
Diarthrosis (Freely Moveable) II Synovial Joint
11
Diarthrosis (Freely Moveable) III
- Many diarthroses also contain accessory
structures - Extracapsular and intracapsular ligaments
- Collateral ligaments of knee
- Cruciate ligaments of knee
- Articular discs
- Meniscus is a pad of fibrocartilage injaw,
wrist, knee and sternoclavicular joints - absorbs shock, guides bone movements
- Bursae
- Found between tendons, muscles, ligaments and
bones - Tendon attaches muscle to bone
- Ligament attaches bone to bone
12
Bursae and Tendon Sheaths
- Bursa is a sac, an extension of joint capsule
that are between nearby structures allowing them
to slide more easily past each other - Tendon sheaths are cylinders lined with synovial
membrane that wrap around a tendon - numerous in hand and foot
- Tenosynovitis inflammation of the tendon sheaths
and synovial membranes - Tendonitis inflammation of _________.
13
TYPES OF DIARTHROSES
14
Ball-and-Socket Joints
- Smooth hemispherical head fits within a cuplike
depression - head of humerus into glenoid cavity of scapula
- head of femur into acetabulum of hip bone
- Multiaxial joint
15
Hinge Joints
- One bone with convex surface that fits into a
concave depression on other bone - ulna and humerus at elbow joint
- femur and tibia at knee joint
16
Saddle Joints
- Each articular surface is shaped like a saddle,
concave in one direction and convex in the other - trapeziometacarpal joint at the base of the thumb
17
Pivot Joints
- One bone has a projection that fits into a
ringlike ligament of another - First bone rotates on the other
- atlantoaxial joint (dens and atlas)
- proximal radioulnar joint
- the radius during pronation and supination
18
Gliding Joints
- Flat surfaces in which bones glide over each other
19
Condyloid (ellipsoid) Joints
- Oval convex surface fits into a concavity
- radiocarpal joint of the wrist
- metacarpophalangeal joints at the bases of the
fingers
20
Special Movements of Diarthroses
- Flexion decreases the angle of a joint
- bending elbow or wrist
- Extension increases the angle of a joint
- Straighten elbow
- Hyperextension is extension of a joint beyond 180
degrees
21
Flexion, Extension Hyperextension
22
Abduction Adduction
- Abduction is movement of a part away from the
midsagittal line -- raising the arm to the side - Adduction is movement adding to midline
23
Abduction Adduction
- Abduction is spreading the fingers away from the
midline (middle finger) - Adduction is movement is returning the fingers to
the anatomical position
24
Elevation and Depression
- Elevation is a movement that raises a bone
vertically - mandibles are elevated during biting clavicles
during a shrug - Depression is lowering the mandible or the
shoulders
25
Protraction Retraction
- Protraction is movement of a bone anteriorly
(forward) on a horizontal plane - thrusting the jaw forward
- scapula
- Retraction is movement of a bone posteriorly
26
Circumduction
- Combines flexion, abduction, extension
adduction - baseball player winding up for a pitch
- NOT Rotation
- (but it looks like it)
27
Lateral and Medial Rotation
- Movement of a bone turning
- rotation of trunk, thigh, head or arm
- Medial rotation turns the bone inwards (internal
rotation) - Lateral rotation turns the bone outwards
(external rotation)
28
Supination/ Pronation
- Occurs in the forearm
- Supination (get soup)
- rotation of forearm so that the palm goes from
the posterior to the anterior - Pronation (pour it out)
- rotation of forearm so the palm goes from
anterior to posterior
29
Inversion Eversion
- Dont use supination and pronation for the feet,
use - Inversion
- raising the medial edge of the foot
- Eversion of foot
- lowering the medial edge of the foot (Adam and
Eve fell)
30
Plantar Flexion Dorsiflexion
- The foot does not extend
- Dorsiflexion is raising of the toes as when you
swing the foot forward to take a step (heel
strike) - Plantarflexion is when the toes point downward as
in standing on tiptoe (or planting a rose between
your toes)
31
Opposition Reposition
- Opposition is movement of the thumb to approach
or touch the fingertips - Reposition is movement back to the anatomical
position - Important hand function that enables the hand to
grasp objects (us vs. apes)
32
The Humeroscapular Joint
- Shoulder is most freely movable joint in the body
- shallowness of glenoid cavity looseness
ofcapsule (golf ball in a shot glass) - Supported by ligaments tendons
- Supported by rotator cuff musculature
- supraspinatus, infraspinatus,
- teres minor subscapularis
- (L is for lateral rotation and
- M is for medial rotation)
33
Tendons of Rotator Cuff MusclesWhere is
dislocation more likely?
34
The Pitcher
- To throw a baseball a pitcher has to use her
shoulder muscles - 1) To ________ to 10 degrees she will use her
supraspinatus muscle - 2) To fully abduct, she will use her _______
muscle - 3) To bring her humerus into lateral rotation she
will use her ______ and _______ muscle - 4) And to throw, she will bring her humerus into
_____ rotation by using her subscapularis muscle.
35
The Elbow Joint
- Single joint capsule enclosing the humeroulnar
and humeroradial joints - Radioulnar and Humeroulnar joint
36
The Hip Joint
- Head of femur articulates with acetabulum
- Socket deepened by acetabular labrum
- transverse acetabular ligament completes labrum
- Blood supply to head of femur found in ligament
of the head of the femur (round ligament)
37
Joint Prostheses
38
The Knee
- Most complex diarthrosis of the body
- patellofemoral gliding joint
- tibiofemoral gliding with slight rotation
gliding possible in flexed position - Joint capsule anteriorly consists of patella
extensions of quadriceps femoris tendon
39
Knee Joint I
- Medial lateral meniscus absorb shock shape
joint
40
Knee Joint II
- The knee has four major ligaments two to limit
sliding from side to side (collaterals) and front
to back (cruciates) - Medial and lateral collateral ligaments prevent
rotation of extended knee and side to side slide - Anterior lateral cruciate ligaments limit
anterior posterior sliding movements (anterior
cruciate is on the anterior of the tibia, the
posterior cruciate is on the posterior _______. - We use the AP draw test to evaluate these
ligament
41
The Ankle Joint
- One joint capsule enclosing the joints between
the talus, tibia and fibula - Groups of ligaments
- deltoid ligament binding the tibia to the foot on
the medial side (never sprained) - lateral collateral ligament binds the fibula to
the foot on the lateral side (most ankle sprains) - achilles tendon inserting on the calcaneus
42
Dissection of Ankle Joint
43
JOINT DISORDERS
- Dislocation (luxation) a total displacement of
a joint with tearing of ligaments, tendons, and
articular capsules (Example shoulder) - Subluxation a slight dislocation causing
structural and neural dysfunction (Example
spine) - Sprain ligament wrenching (i.e. sprained ankle)
- torn ligaments or tendons
- Strain muscle over stretching
44
Arthritis
- Arthritis is a broad term for pain inflammation
- Blood test may make the diagnosis and/ or X-ray
findings - Gouty arthritis
- Involves sodium urate crystals deposited in soft
tissues of joints, causing inflammation,
swelling, and pain - Major features Great toe, One joint, Uric acid
increased, Temperature dependent - Osteoarthritis results from years of joint wear
- articular cartilage softens and degenerates
- accompanied by crackling sounds called crepitus
- bone spurs develop on exposed bone tissue causing
pain - Rheumatoid arthritis is autoimmune attack on
joint - antibodies attack synovial membrane, enzymes in
synovial fluid degrade the cartilage, bones
ossify, remissions occur
45
Rheumatoid Arthritis
46
Rheumatoid Arthritis