Bacterial Cell Structure (continued) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Bacterial Cell Structure (continued)
Description:
Title: Effect of osmotic pressure on cells Author: DGILMORE Last modified by: DGILMORE Created Date: 1/24/2004 6:45:31 PM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:205
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Bacterial Cell Structure (continued)
1
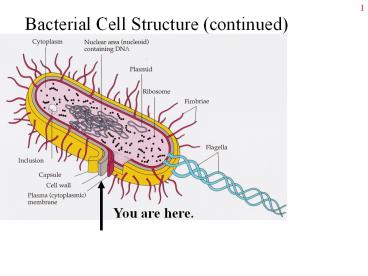
Bacterial Cell Structure (continued)
You are here.
2
Gram negative cell wall
3
Outer membrane
- Lipid bilayer membrane Asymmetric
- Inner and outer leaflets
- Inner leaflet made of phospholipids outer
leaflet is made of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) - LPS endotoxin
- Proteins for transport of substances
- Porins tri-subunit, transmembrane proteins
- Barrier to diffusion of various substances
- Lipoprotein anchors outer membrane to PG
4
Structure of LPS
extends from cell surface.
contains odd sugars e.g. KDO.
Gln-P and fatty acids take the place of
phospholipids.
www.med.sc.edu85/fox/ cell_envelope.htm
5
Periplasmic Space
www.arches.uga.edu/emilyd/ theory.html
6
Periplasm
- The periplasm is the stuff in that space,
present in Gram bacteria also. - A hydrated gel including the PG
- Binding proteins that aid in transport
- Hydrolytic enzymes for breaking down large
molecules - Chemoreceptor proteins that help direct swimming
- Enzymes for synthesizing PG, OM
7
Glycocalyx capsules and slime layers
Sugar covering capsules are firmly attached,
slime layers are loose.
Multiple advantages to cells prevent
dehydration absorb nutrients protection from
predators, WBCs protection from biocides (as
part of biofilms) attachment to surfaces and
site of attachment by others. S-layers are
highly structured protein layers that function
like capsules
cell
capsule
www.activatedsludge.info/ resources/visbulk.asp
8
Fimbriae and pili
Both are appendages made of protein Singular
fimbria, pilus Both used for attachment Fimbriae
to surfaces (incl. host cells) and other
bacteria. Pili to other bacteria for exchanging
DNA (sex).
www.ncl.ac.uk/dental/oralbiol/ oralenv/images/sex1
.jpg
9
Fimbriae and pili-2
http//www.mansfield.ohio-state.edu/sabedon/006pi
li.gif
10
Flagella
- Flagella protein appendages for swimming through
liquid or across wet surfaces. - Rotate like propellers.
- Different from eukaryotic flagella.
- Arrangements on cells
- polar,
- Lophotrichous,
- amphitrichous,
- peritrichous.
www.ai.mit.edu/people/ tk/ce/flagella-s.gif
www.bmb.leeds.ac.uk/.../icu8/ introduction/bacteri
a.html
11
Flagellar structures
www.scu.edu/SCU/Departments/ BIOL/Flagella.jpg
img.sparknotes.com/.../monera/ gifs/flagella.gif
12
Runs and Tumbles bacteria find their way
http//www.bgu.ac.il/aflaloc/bioca/motil1.gif
13
Motility revisited
- Flagella protein appendages for swimming through
liquid or across wet surfaces. - Axial filament a bundle of internal flagella
- Between cell membrane and outer membrane in
spirochetes - Filament rotates, bacterium corkscrews through
medium - Gliding
- No visible structures, requires solid surface
- Slime usually involved.
14
Axial filaments
http//images.google.com/imgres?imgurlhttp//micr
ovet.arizona.edu/Courses/MIC420/lecture_notes/spir
ochetes/gifs/spirochete_crossection.gifimgrefurl
http//microvet.arizona.edu/Courses/MIC420/lecture
_notes/spirochetes/spirochete_cr.htmlh302w400
sz49tbnidBOVdHqepF7UJtbnh90tbnw119start1
prev/images3Fq3Daxial2Bfilament2Bbacteria26
hl3Den26lr3D26sa3DG
15
Gliding Motility
Movement on a solid surface. No visible
organelles of locomotion. Cells produce, move in
slime trails. Unrelated organism
glide myxobacteria, flavobacteria,
cyanobacteria appear to glide by different
mechanisms. Cells glide in groups, singly,
and can reverse directions.
http//cmgm.stanford.edu/devbio/kaiserlab/about_my
xo/about_myxococcus.html
16
From the membrane in the bacterial cytoplasm
- Cytoplasm is a gel made of water, salts, LMW
molecules, and lots of proteins. - DNA nucleoid, w/ proteins
- Plasmids small circular DNA
- Ribosomes site of protein synthesis.
Cytoplasm may also contain inclusions, gas
vacuoles, extended membrane systems, or
magnetosomes. But generally NO membrane-bound
organelles.
17
Inclusions and granules
- Storage molecules found as small bodies within
cytoplasm. - Can be organic (e.g. PHB or glycogen) or
inorganic (Sulfur, polyphosphate. - PHB, a type of PHA, degradable plastic
(polyester) glycogen, a polymer of glucose. - Sulfur, a metabolic by-product polyphosphate,
polymer of PO4
http//www.accessexcellence.org/WN/SUA12/marg499.h
tml
18
Magnetosomes
Membrane coated pieces of magnetite, assist
bacteria in moving to microaerophilic
environments. An organelle? North is down.
Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum
www.calpoly.edu/rfrankel/ mtbphoto.htmlhttp//ge
oweb.tamu.edu/courses/geol101/lab/topo_maps/IMG000
06.GIF