Automated sequencing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
Automated sequencing
Description:
Zwichel is a microtubule base motor protein (kinesin). Kinesins form mostly homo or heterodimers. They are characterized by their N-or C-terminal motor domain. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:66
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Automated sequencing
1
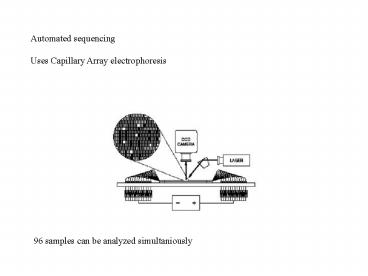
Automated sequencing Uses Capillary Array
electrophoresis
96 samples can be analyzed simultaniously
2
Also known as BAC by BAC approach
PHYSICAL MAP
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
Also known as BAC by BAC approach
7
whole genome shotgun sequencing
Advantage less work Disadvantage more gaps in
final assembly
8
Positional cloning general strategy
If lt 1 cM apart
average of 12 candidate genes
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Study determinants cell shape Model system
Trichome
15
- Screening for trichome morphogenesis mutants
- Two groups
- Branching mutants
- Elongation/Maturation mutants
- We used the two groups to analyze phenotype,
expression pattern, identification of one of the
mutants
16
Class Two Elongation/Maturation
17
Figure from hussey review
18
BRK1 experession The When, Where and How
(strong)
Northern Blot
RT-PCR
19
Cytoskeleton components
20
Actin branching
21
ABD2GFP protein fusion
Reports the localization of actin
Wild type
brk1
Differences in actin distribution actin more
bundled in brk1
22
Drosophila S2 cells spread on coated glass
surface via actin dependent lamellipodia
RNAi experiment to determine the effects of
Arp2/3 components in animal cells Defects in
actin distribution Defects in adhesion and cell
shape
23
Class 2 Branching phenotype
We used only frk from this panel, the others we
did not use
24
x
Allelism Tests
How many genes are involved?
M3 plant mut-1/mut-1
M3 plant mut-2/mut-2
Legend
Case 1
Case 2
Mutant phenotype
mut-1/mut-2 Allelism Single gene
mut-1/ mut-2/ No allelism Two genes
Wild-type phenotype
Mutants 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 were crossed Mutants
1 and 3 mut allelic 3 different genes Mutants 2
and 6 mut allelic
25
LINKAGE, CROSSOVER AND MAPPING IN
EUKARYOTES Mapping what does that mean? It
means determining the unknown locus or position
of a gene within the genome relative to other
genes or DNA regions used as markers. T
he Arabidopsis genome has 5 chromosomes as you
know from the TAIR exercise. We want to find the
position of the gene mutated in mutant 1
mut1 ?
26
Col
Ler
Variable number of repeats of a certain sequence
(e.g. GA) characterize SSLP markers
Mutation 1 was linked to chromosome 5
27
CAPS markers are characterized by the presence of
a restriction site in one allele and the absence
of the restriction site in another allele
Map until you find 0 recombinants with one
molecular marker Mapped mutation one to BAC
K14B20
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)
30
Genes on K14B20 are candidates for mutation1 Do
T-DNA lines exist for any of the genes annotated
for BAC K14B20 and if so do they these plants
show a mutant phenotype ?
not all genes of K14B20 are on this presentation
31
T-DNA insertion lines
32
wild type zwi
At5g65930 SALK_13
wild type
zwi
33
Sequencing of ZWI in mutants 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6
Mutant 1 and 3 zwi alleles
34
(No Transcript)
35
ZWICHEL is a kinesin (motor protein)
36
Cytoskeleton components
37
Global expansion
Polar expansion
Mathur, 2006
38
ZWI ?
BRK1 ARP2/3
Mathur, 2006