Copy this diagram on Portfolio p6 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Copy this diagram on Portfolio p6
Description:
... and established an English colony called Plymouth. 0 The Magna Carta (1215) The king s powers were limited Free men ... newspaper publisher John Peter Zenger ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:42
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Copy this diagram on Portfolio p6
1
Copy this diagram on Portfolio p6
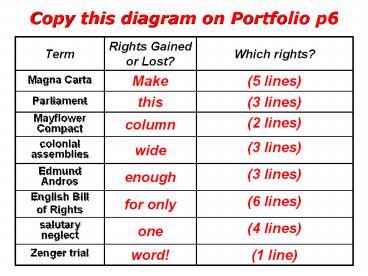
Term Rights Gained or Lost? Which rights?
Magna Carta Make (5 lines)
Parliament this (3 lines)
Mayflower Compact column (2 lines)
colonial assemblies wide (3 lines)
Edmund Andros enough (3 lines)
English Bill of Rights for only (6 lines)
salutary neglect one (4 lines)
Zenger trial word! (1 line)
2
Lesson 5.2 Roots of Representative Government
- Today we will trace the expansion of the rights
of English subjects and discuss early
self-government in the colonies.
3
Vocabulary
- trace follow a sequence of events in
chronological order - compact a legal agreement a contract
- bicameral describes a legislative body with two
houses or branches - assembly group of people brought together to
perform a function, especially to make laws
4
Check for Understanding
- What are we going to do today?
- How would someone trace your movements through
the day? - How many houses are in a bicameral legislature?
- What is the job of the the state assembly in
Sacramento?
5
What We Already Know
- In 1215, a group of English barons forced the
English King John to sign the Magna Carta, a
document which limited his powers and protected
their privileges.
6
What We Already Know
- Since the voyages of Columbus, Europeans had
begun establishing colonies in North America.
7
What We Already Know
- In 1620, the Mayflower was blown off course and
landed off Cape Cod on the Massachusetts coast
(instead of Virginia, where they were supposed to
go) and established an English colony called
Plymouth. - 0
8
The Magna Carta (1215)
- The kings powers were limited
- Free mens property rights protected
- Taxation only with the consent of a council of
prominent men - No trial without witnesses
- Trial by jury of peers
- Over time, these rights were extended to all
Englishmen.
9
Changes in Parliament
- Parliament was the group that made laws for the
English people. - Parliament was bicameral, and it consisted of a
House of Lords and a House of Commons. - Members of the noble class inherited seats in the
House of Lords. - Ordinary Englishmen were given the right to elect
members to the House of Commons.
10
7. What were four rights granted by the Magna
Carta?
- Protection against being taxed without the
consent of a council of leading men - Right to own firearms
- Protection against their property being seized by
the king or his officials - Freedom of the press.
- Trial by a jury of their peers
- Trial based on witnesses, not merely accusations
of officials.
Choose all that are true!
11
9. How did Parliament serve as a model for
colonial governments, and for Congress later?
- It was an elected, bicameral legislative body.
- All citizens participated in making new laws.
- Its members were appointed by the king.
- It had veto power over the executive branch.
12
The Mayflower Compact
- For the sake of order, the men aboard the
Mayflower signed an agreement called the
Mayflower Compact in 1620. - In it, they vowed to obey laws agreed upon for
the good of the colony. - The Mayflower Compact helped establish the idea
of self-government and majority rule.
13
Colonial Representative Assemblies
- The king and Parliament were too far away to
manage every detail of the colonies, and English
colonists wanted to have a say in making the laws
that governed them. - Colonists were allowed to elect men to colonial
assemblies, which could make laws to govern the
colonies.
14
Colonial Representative Assemblies
- Virginias House of Burgesses was the first
colonial assembly, but the assemblies power was
limited . - Their laws only had power within their colonies,
and these laws had to be approved by the
governor, who usually was appointed by the king. - Colonists could not elect representatives to
Parliament, so they had no input on new laws. - Colonists disliked some of the laws that affected
the colonies, and they also began to clash with
royal governors.
15
10. How was representative government limited in
the colonies?
- The English king and Parliament still had power
over colonial assemblies. - Colonial assemblies had to submit all their laws
to the king for approval. - Only members of Parliament could serve in the
colonial assemblies. - Only landowners could serve in the colonial
assemblies.
16
13. In what two ways could the royal governor
stop the colonial assembly from making laws he
disliked?
- He had final approval on all laws passed by the
colonial assembly. - He appointed all the members of the colonial
assembly. - He could dismiss the colonial assembly to prevent
them from passing laws. - He conducted all the trials in the colony and
could influence the jury's verdict.
Be sure to choose TWO that are true!
17
Edmund Andros
- 1685 New king James II cracked down on colonial
smuggling. - James created Dominion of New England by
combining Massachusetts with other New England
colonies.
18
Edmund Andros
- James II appointed Andros as governor of the
Dominion. - Andros angered colonists by shutting down
colonial assemblies and by suspending jury
trials. - When colonists protested their loss of rights by
refusing to pay their taxes, Andros had them
jailed.
19
The English Bill of Rights
- Parliament overthrew James II in 1688, and
replaced him with his daughter Mary and her
husband, William of Orange. - William and Mary agreed to the English Bill of
Rights, which built upon the Magna Carta and
strengthened the rights of the people.
20
The English Bill of Rights
- No laws cancelled or taxes imposed without the
consent of Parliament - Free elections and frequent meetings of
Parliament to be held - No excessive fines or cruel punishments
- People could complaining to the king in
Parliament without fear of arrest
- The Bill of Rights established the important
principle of the government being based on laws
made by Parliament, not on the desires of a
ruler.
21
8. What do The Magna Carta, the English Bill of
Rights, and the Mayflower Compact have in common?
- All were laws created to expand the power of the
king of England. - All were laws created by the English Parliament.
- All gave the people more protection against the
king's power. - All served as models for the Constitution's Bill
of Rights.
22
The English Bill of Rights
- In Boston, after hearing that James had fallen,
American colonists arrested Andros and Parliament
restored their colonial assemblies. - Royal governors could still veto laws passed by
the assemblies, but they paid the governors
salary. - If a governor blocked the assembly, the assembly
might refuse to pay him.
23
Salutary Neglect
- During the first half of the 1700s, England
interfered very little in colonial affairs. - Parliament passed laws but they were rarely
enforced in the colonies. - During this period of salutary neglect, colonists
got used to acting on their own.
24
The Zenger Trial
- In 1735, newspaper publisher John Peter Zenger
was on trial for printing criticism of New Yorks
governor. - Zengers lawyer argued that people had the right
to speak the truth. The jury agreed, and he was
released. - The Zenger trial helped establish the freedom of
the press to print the truth.
25
11. How did Englands policies toward the
colonies change after the Glorious Revolution?
- England gave the colonies much more
self-government. - England made Catholicism the official religion of
the colonies. - The new monarchs strengthened the rights of all
citizens, both at home and in the colonies. - England began allowing the colonies to send
representatives to Parliament.
26
12. What is salutary neglect?
- A period of time in which colonial assemblies
were banned by Parliament. - A period of time in which Parliament raised taxes
dramatically on trade in the colonies. - A period of time in which the English king lost
more and more power to Parliament. - A period of time in which England did not
interfere much in colonial affairs.
27
14. What right grew from the trial of John Peter
Zenger?
- Religious freedom
- Freedom from self-incrimination
- Freedom of the press
- Protection from illegal search and seizure
28
Term Rights Gained or Lost? Which rights?
Magna Carta Gained Property cant simply be seized No tax without a councils agreement No trial without witnesses Trial by jury of peers
Parliament Gained Englishmens right to elect representatives to Parliament
Mayflower Compact Gained Puritans established self-government and majority rule
colonial assemblies Gained Colonists right to elect representatives to their assemblies
29
Term Rights Gained or Lost? Which rights?
Edmund Andros Lost Colonists right to elect representatives
English Bill of Rights Gained No laws cancelled or taxes imposed without the consent of Parliament Free elections and frequent meetings of Parliament No excessive fines or cruel punishments Rights to complain to the king in Parliament
salutary neglect Gained Increased rights to self-government
Zenger trial Gained Freedom of the press





![Download Book [PDF] How to Trade Options: The Complete Guide for Beginners (2nd Edition) (Options PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10099122.th0.jpg?_=20240815027)
























