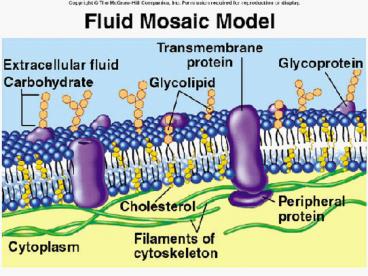
CELLULAR TRANSPORT - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
CELLULAR TRANSPORT
Description:
CELLULAR TRANSPORT What gets in and what gets out? Passive Transport 1- Diffusion - occurs when there is an unequal concentration of molecules on one side of the cell ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:181
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: CELLULAR TRANSPORT
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
CELLULAR TRANSPORT
- What gets in and what gets out?
4
(No Transcript)
5
Passive Transport
- 1- Diffusion - occurs when there is an unequal
concentration of molecules on one side of the
cell compared to the other. The molecules move
from the area of high concentration to an area of
lower concentration until a dynamic equilibrium
is reached. - USED BY Small Hydrophobic Molecules O2 ,CO2, N2
- activity
6
Diffusion
7
Passive Transport
- 2 Osmosis - the diffusion of water through a
selectively permeable membrane. The membrane is
permeable to water, but impermeable to the larger
molecules. Water diffuses from an area of high
water concentration to an area of lower water
concentration until the equilibrium between water
and solute is reached. - USED BY H2O
- demo
8
(No Transcript)
9
Passive Transport
- 3 - Facilitated diffusion Gatekeeper proteins
open and close paths through the cell membrane
allowing some molecules to pass freely. It allows
materials to move in and out of the cell much
more quickly than regular diffusion and does not
require energy from the cell. - USED BY Glucose. Diffuses into red blood cells
faster than other similar sugars.
10
(No Transcript)
11
Active Transport
- The movement of materials from an area of lower
concentration to an area of higher concentration
by expending energy is called active transport. - Carrier proteins receive energy that allows them
to aid in active transport.
12
Active Transport
- 1 Transport Carrier Proteins Proteins open
and close paths through the cell membrane
allowing some small solutes to pass through.
Energy is required to transport the solutes
against the concentration gradient. - USED BY Sodium-potassium pump
13
Animation and quiz http//highered.mheducation.com
/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation
__how_the_sodium_potassium_pump_works.html
14
Active Transport
- 2 Endocytosis the process by which cells
ingest materials. - Large molecules can not pass through the cell
membrane. - The particle pushes against the membrane and
forms an indentation. The cell membrane wraps
around the particle and engulfs it into a
vacuole. - Often enzymes from lysosomes are then used to
digest the molecules.
15
Active Transport
- 2a Pinocytosis the process of engulfing
dissolved molecules. - USED BY fat droplets engulfed by cells of the
small intestine
16
(No Transcript)
17
Active Transport
- 2b Phagocytosis the process of engulfing
solid particles. Can be used to engulf whole
cells. - USED BY invading microbes engulfed by white
blood cells
18
(No Transcript)
19
Active Transport
- 3 Exocytosis the process by which large
molecules in the cell are transported to the
external environment. - Materials are contained in vesicles. The
vesicles fuse with the membrane and then the
material is released. - USED BY waste materials released from the cell.
Transmitter chemicals emitted from nerve cells.
20
(No Transcript)
21
Organizer
- Make a chart to organize the following key terms
- Cellular transport
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Facilitated diffusion
- Active transport
- Endocytosis
- Transporters
- Passive transport
- Exocytosis
22
Questions
- Why are cell membranes a bilayer?
- Why are proteins important for the functioning of
a cell? Provide examples - Why are cells so small?
- Compare and contrast
- Passive Active transport
- Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion
- Diffusion and Osmosis
- Why must tissues used in medical procedures be
bathed in a solution of the same osmolarity as
the cytoplasm?
23
Reference images
- http//faculty.southwest.tn.edu/rburkett/GB1-osmos
is.htm