Structure of the Earth - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Structure of the Earth
Description:
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:212
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Structure of the Earth
1
Structure of the Earth
2
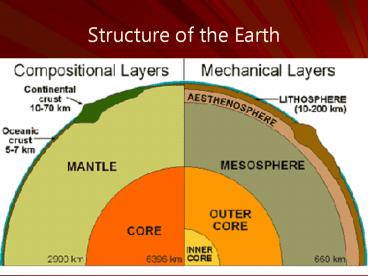
Compositional (Chemical) Layers
- Crust Low density
- High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O)
- Moho Density boundary between crust and
mantle - Mantle Higher density
- High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe)
- Core High in Nickel (Ni) and Iron (Fe)
3
Earth The Giant Magnet
- Magnetic field created by liquid iron convecting
in outer core.
4
(No Transcript)
5
- Magnetic field directs solar winds (ionized
particles) around the Earth or to the poles.
6
Aurora Borealis
7
Heat Flow in the Earth
- Heat sources
- latent heat from the formation of the Earth
- Radioactive decay in the core and mantle
- Temperature at core 3000-5000 C
- Cooling processes
- Convection currents
- Plate tectonics (volcanoes)
8
(No Transcript)
9
Mechanical (Physical) Layers of the Earth
Lithosphere Crust and upper, solid part of the
mantle plates in plate tectonics Asthenosphere
Partially molten part of mantle location of
convection current that drive plates Outer core
Liquid Inner core Solid
Greatest temperatures, solid due to intense
pressure
10
Evidence for Structure of the Earth
- Seismic (earthquake) waves
- P waves (Primary) Longitudinal (compressional)
waves faster, can move through any matter - S waves (Secondary) Transverse waves. Can only
travel through solid matter.
11
Evidence for Structure of the Earth Cont.
- S waves can not travel through the outer core.
12
Rock Types
- Igneous Solidified molten magma
- 2 types of Igneous
- Extrusive (volcanic) erupted lava
- Cools more quickly, so only small crystals
form. - Intrusive (plutonic) never erupted magma
- Cools more slowly within the earth, so larger
crystals can form.
13
- Quartz Silica (SiO2), light color. Magma high
in silica is viscous. - High silica magma found in more explosive
volcanoes due to build up of pressure with more
viscous magma. - Forms stratovolcano (cone shape)
- Low silica magma found in less explosive
volcanoes. - Form shield shape.
14
Extrusive Igneous Rock
Basalt Andesite Rhyolite
Low in silica High in Silica
Black Pale pink, grey
15
Intrusive Igneous Rock
Gabbro Dacite Granite
Low in Silica High in Silica
Black Pale Grey, pink
16
Sedimentary Rock
- Sedimentary rock formed by compaction of
sediments. Classified by particle size.
Shale
Sandstone
17
Sedimentary Rock cont.
- Almost all fossils found in sedimentary rock
- Almost all fossil fuels (coal, oil, gas) found in
sedimentary rock.
18
Metamorphic Rock
- Metamorphic rock is rocked that has been
changed by heat and/or pressure. - Caused by burial and proximity to volcanic
areas. - Dense, often streaks/folds
- Many gemstones are metamorphic.
19
Rock Cycle