Circulatory System PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title: Circulatory System
1
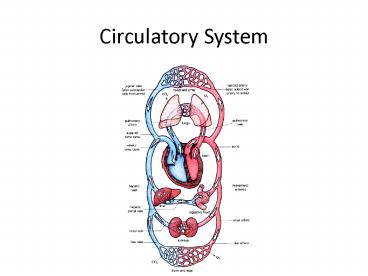
Circulatory System
2
Purpose of Circulatory System
- Transport materials within the body
- Oxygen, carbon dioxide, biomolecules
3
What does the circulatory system transport?
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
- Doughnut-shaped
- Contains hemoglobin- complex protein containing
iron that transports oxygen
4
Other Blood Cells
- White Blood Cells
- Immune response
- Platelets
- Blood clotting
5
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vcKX2gAJX7josafety_
modetruepersist_safety_mode1 - http//www.youtube.com/watch?vlrYlZJiuf18safety_
modetruepersist_safety_mode1 - http//www.youtube.com/watch?v--bZUeb83uUfeature
relatedsafety_modetruepersist_safety_mode1
6
Plasma
- Watery portion of the blood
- Carries digested food particles to cells
7
Types of Blood Vessels Arteries
- Arteries
- Away from the heart
- Thick muscular walls
8
Types of Blood Vessels Veins
- Veins
- Toward the heart
- Contains valves to prevent
- backflow of blood
9
Types of Blood Vessels Capillaries
- Capillaries
- Smallest blood vessels
- Most restricted of blood vessels
- Only allow 1 red blood cell through at a time
http//www.youtube.com/watch?vQ530H1WxtOwsafety_
modetruepersist_safety_mode1
10
The Heart
11
Blood Flow Through the Heart
12
Coronary Circulation
- Coronary Circulation Circulation of blood to
heart muscle cells
13
Pulmonary Circulation
- Pulmonary circulation Circulation between the
lungs and the heart
Oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in
pulmonary circulation
14
Systemic Circulation
Systemic Circulation Carries blood to rest of
the body
Deoxygenated blood ENTERS the heart from the body
via the superior and inferior Vena Cavas
Oxygenated blood LEAVES the heart to go to the
rest of the body via the aorta
Blood goes back to the heart from the lungs-
heart pump provides enough force for blood to
travel through the rest of the body
15
Systolic vs. Diastolic Pressure
- Systolic Pressure
- Ventricle contracts
- Blood forced into the arteries
- More pressure on walls
- Artery walls expand
- Diastolic Pressure
- Ventricle relaxes
- Less blood in arteries
- Less pressure on walls
- Arteries walls relax
http//www.youtube.com/watch?v2A_wy8r93osfeature
relatedsafety_modetruepersist_safety_mode1
16
Lymphatic Circulation
- Removes extra fluid between cells (interstitial
fluid) - Transports immune cells
- Immune response
- Large of white blood
- cells are found in the lymph
- nodes where bacteria
- are destroyed
17
Cardiovascular Diseases
- Anemia- too few red blood cells
- Atherosclerosis- fatty deposits on the walls of
arteries - Caused by high cholesterol
- Hardens
- Narrower opening for blood to get through
- Heart attack- blood vessel to heart is blocked