The Na -K ATPase Pump - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
The Na -K ATPase Pump
Description:
... gating of ion channels The technique of patch clamp recording Measuring Ion Channel Conductance Patch Clamp Recording Patch Clamp Recording The ionic basis of ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1860
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Na -K ATPase Pump
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
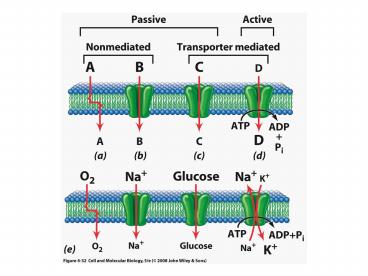
The Na-K ATPase Pump
4
Cardiac glycosides
plant and animal steroids
Ouabain!
Digitalis! increased Na conc inside
heart leads to stimulation of Na-Ca2 exchanger,
which extrudes sodium in exchange for inward
movement of calcium. Increased intracellular
Calcium stimulates muscle contraction.
5
The Na-K ATPase Pump Mechanism
6
Response of a human RBC to changes in
osmolarityof the extracellular fluid
7
The Na-K ATPase Pump is
required to maintain
Osmotic Balance and Stabilize Cell Volume
Sources of Intracellular Osmolaritylarge
number of counterions (inorganic ions of opposite
charge) that are attracted to large
macromolecules (most are charged).small
metabolites (high concentration of small organic
molecules, sugars, amino acids, nucleotides) and
their counterions
Sources of Extracellular Osmolarity Due
mainly to small inorganic ions - these leak
slowly across the plasma membrane into the cell.
The problem Because of above
factors, water moves into the cell by osmosis
The
Solution
Na-K
ATPase Pump
8
In vitro Investigation of The Na-K ATPase Pump
9
Control of acid secretion in the stomach
10
Potassium channel
11
(No Transcript)
12
The Potassium Channel
13
Hinge-bending Model for the opening of the
Bacterial KcsA Channel.
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
The Structure of One subunit of a eukaryotic,
Voltage Gated K Channel (Drosophila Shaker K
Channel)
17
3-D Structure of a Voltage Gated Mammalian K
Channel
18
(No Transcript)
19
Conformational States of a Voltage Gated K Ion
Channel
20
A typical ion channel fluctuates between open and
closed states
21
The gating of ion channels
22
The technique of patch clamp recordingMeasuring
Ion Channel Conductance
23
Patch Clamp Recording
24
Patch Clamp Recording
25
(No Transcript)
26
The ionic basis of membrane potential
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
The membrane potential in animal cells depends
mainly on K Leak channels and the K gradient
across the plasma membrane
34
dGconc -RT ln Co Ci
35
dGvoltzFV
36
dGconc dGvolt 0Ion distribution is at
equilibrium across the membrane
37
The Nernst Equation and Ion FlowV RT ln Co
zF Ci
38
The Resting Potential decays only slowly when the
Na K Pump is stopped