Chromosome Mutation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Chromosome Mutation
Description:
Chromosome Mutation – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1119
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
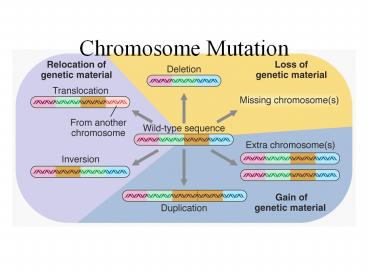
Title: Chromosome Mutation
1
Chromosome Mutation
2
Ploidy Euploids
- Number of chromosome sets
- Ancestral polypoloidation thought to be common
(Fig 11-3) - Haploid n 8 somatic chr 8 meiosis 8
bivalents - Monoploid n 8 somatic chr 8 (but species
chr 16) gametes by mitosis - Diploid n 8 somatic chr 16 meiosis 8
bivalents - Triploid n 8 somatic chr 24 meiosis 8
trivalents or 8 bivalents 8 univalents - Autotetraploid n 8 somatic chr 32
meiosis 16 bivalents or 8 tetravalents (8
homologs) - Allotetraploid n 8 somatic chr 32
meiosis 16 bivalents (16 homologs 8 homeologs)
3
Euploidy Meiotic Chromosome Alignments
4
Changes in Ploidy in plant breeding
5
Development of Hexaploidy in Modern Wheat
6
Aneuploidy
7
Effect of Maternal Age on Trisomy 21
8
Loss of pairing Both homologs can go to the same
pole Loss of cohesionOne homolog and one
sister chromatid of the other homolog can go to
the same pole
9
Monosomy for X Turner Syndrome
10
XXYKlinefelter Syndrome
11
Mechanisms of Chromosome Rearrangements
12
Mechanisms of Chromosome Rearrangements
13
Inversion loop at meiosis in an Inversion
Heterozygote
14
Inversion loop at meiosis in an Inversion
Heterozygote
15
Drosophila Polytene Chromosomes allow inversion
and deletion loops to be visualized
16
Generation of acentric and dicentric chromosomes
by meiotic recombination in inversion
heterozygotes