Inadequate Blood Circulation In The Kidneys PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Anemia and Heart Failure: Cognition, Affect, and Functional Status Susan G. Nayfield, M.D., M.Sc. Geriatrics and Clinical Gerontology Program National Institute on Aging
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Depression associated with increased risk of anemia (OR1.93; 95% CI 1.19-3.13) ... Depression, acute psychosis ('megaloblastic madness') Risk of stroke (homocysteine) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 21: Blood Vessels and Circulation Primary sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology. 6th ed. San Francisco: Pearson Benjamin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... filled spaces; some have extra large fenestrations, allow proteins and blood cells to enter ... receptors (baroreceptors), in large arteries above heart ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
BLOOD & FLUIDS Intermediate Lecture - Blood A&P * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * HEMOSTASIS ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 23 Circulation
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Oxygen (O2) and nutrients diffuse across capillary walls and enter tissues ... Color varies from scarlet to dark red. The pH of blood is 7.35 7.45. Temperature is 38 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Heart Circulation & Physiology Ch. 18
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
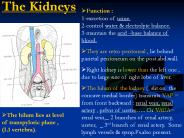
The Kidneys Function : 1-excretion of urine. 2-control water & electrolyte balance.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 21: Blood Vessels and Circulation Last modified by: Carla Gollwitzer Created Date: 3/18/2005 4:18:50 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Blood diseases. Dr. Abed M. Al Hazmi. Associated prof. of pediatrics. King A/Azziz University Jeddah KSA.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Oxygen (O2) and nutrients diffuse across capillary walls and enter tissues ... Heme and globin are separated and the iron is salvaged for reuse ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Blood cells and most proteins are too big to get through. Bulk flow: ... Hydrostatic pressure: lateral pressure component that pushes fluid through capillary pores ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
An organism, which reachs heart beating and blood circulation, but does not develop beyond ... renders an organism inadequate to be animated by a human soul. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Veins have much lower blood pressure and thinner walls than arteries ... Blood Pressure (BP) ... Blood pressure in elastic arteries near the heart is pulsatile ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 20: Blood Vessels & Circulation. I. General Anatomy ... Minor role in adjusting vessel diameter via vasomotor center. Medullary ischemic reflex: ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Interpretation of Blood Gases Chapter 7 Blood Gas Analyzers Accurate measurements of pH, PCO2, PO2 Electrodes Sanz electrodes Severinghaus electrodes Clark electrodes ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Nature of Disease Pathology for the Health Professions Thomas H. McConnell Chapter 8 Disorders of Blood Vessels Lecture 8
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 17: Blood Overview Blood functions Compostion of whole blood Plasma RBCs structure, function, and development Blood types WBCs Platelets Hemostasis The ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
An ideal and healthy blood pressure range is more than 90/60 mmHg and less than 120/80 mmHg. Read the blog to find out why one should have ideal blood pressure.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chest X-ray: mediastinal node and lung involvement. Bone changes. Medical ... Promote lymph drainage (elevate, compression hose) No cure. Malignant lymphoma ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Mean blood pressure is controlled by changing total peripheral resistance and or ... ( Frank-Starling mechanism: reduced LV contractile force) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
How do we describe blood and the RBCs found in it? ... How long do RBCs last in the circulation? ... Why is EPO popular for athletes in the Tour De France? ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 18 The Circulatory System: Blood Blood Functions and properties Blood cell production Erythrocytes (RBC) Leukocytes (WBC) Hemostasis Blood types
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Biology 221 Anatomy & Physiology II TOPIC 1 Circulatory System Blood Chapter 17 pp. 644-674 E. Lathrop-Davis / E. Gorski / S. Kabrhel Major Components Blood Heart ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Blood is carried in a closed system of vessels that begins and ends at ... Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
List the potential clinical and pharmacoeconomic benefits of current blood ... 3.08 days for an apheresis platelet unit. Average cost of RBC units increased by 30.8 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
It's one of the rules we kept from the Jewish tradition. ... Then the baby might be born with Hemolytic disease of the new born (HDN), a type of anemia ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cardiovascular System: The Integrated System for Blood Pressure Regulation Mary Christenson, PT, PhD DPT 732 Management Applications of Physiology II
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
UNIT 1 Blood - Part 1 of 2 Overview of Blood Plasma Formed Elements: RBCs and WBCs (8th edition) How to use your PowerPoint lectures This PowerPoint lecture follows ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Blood loss, Hypothermia and Transfusion in the Burn O'R'
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
DeepDown Detox: Targeted programs for the kidneys, lungs, skin, cells and colon
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Occlusive essentially blocked arteries. Outline. Review of the circulation ... May cause symptoms and signs particularly when more blood flow is required; ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Prolonged cessation of epicardial blood flow results in damage to ... Inadequate cardiac scar. Process NOT an immediate event on reperfusion ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Circulation of blood through an organ structure. Delivers oxygen and nutrients and ... Treatment for epistaxis (nose bleed) Treatment for epistaxis (nose bleed) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Acute Renal Failure (ARF) is the sudden loss of kidney functionality. The causes of ARF are classified into three categories such as prerenal, renal, and postrenal. Prerenal ARF is caused by problems that affect the flow of blood, before it enters the kidneys. Postrenal ARF is caused by problems in passing of urine out of the kidneys. Renal ARF is caused by problems with the kidney itself, resulting in the improper filtration of blood or disrupted production of urine.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Acute Renal Failure (ARF) is the sudden loss of kidney functionality. The causes of ARF are classified into three categories such as prerenal, renal, and postrenal. Prerenal ARF is caused by problems that affect the flow of blood, before it enters the kidneys. Postrenal ARF is caused by problems in passing of urine out of the kidneys. Renal ARF is caused by problems with the kidney itself, resulting in the improper filtration of blood or disrupted production of urine.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Acute Renal Failure (ARF) is the sudden loss of kidney functionality. The causes of ARF are classified into three categories such as prerenal, renal, and postrenal. Prerenal ARF is caused by problems that affect the flow of blood, before it enters the kidneys.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Saladin Ch. 20 Blood Vessels
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Oxygen (O2) and nutrients diffuse across capillary walls and enter tissues ... Pernicious anemia results from: Deficiency of vitamin B12 ...
Exercise increases blood serum serotonin levels. An increase in serotonin levels can positively impact mood, social behavior, appetite, digestion, memory, sexual function and improve sleep. Glucagon and insulin, both secreted by the pancreas, act antagonistically to each other in order to maintain blood glucose levels.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Soft substance in core of bones. Blood cell production (Hematopoiesis) ... Monitor stool, urine and emesis for occult blood. Diet teaching foods rich in iron ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Blood ... Blood pressure. Orthostatic hypotension. Lungs: Dyspnea / added ... Glomerular blood flow and pressure. Only about 50% develop oliguria. Can last ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Regulation of cardiac activity Cardiac output Blood flow Blood pressure Blood pressure also regulated by: Atrial stretch receptors ADH release Renin-angiotensin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Blood Supply of Mature Bones 3 sets of blood vessels develop Nutrient artery and vein: a single pair of large blood ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... After Every Patient Use In general, ... quality in their words, radiation ... Defibrillation Defibrillation Safety Return of Spontaneous Circulation ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
SHOCK SHOCK DEFINTION The common denominator in all forms of shock is inadequate capillary perfusion. Shock is Characterized by Inadequate Tissue Perfusion and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... by hematocrit (percentage of the total blood volume composed of red blood cells) ... Greater resistance is encountered in longer tubes than in shorter tubes ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The laboratory measurement of blood gases and pH involves the use of special ... Laboratory tests on blood samples include the measurement of arterial CO2 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Biology 221 Anatomy & Physiology II TOPIC 4 Circulatory System Blood Flow, Blood Pressure & Capillary Dynamics Chapter 20 pp. 727-747 E. Lathrop-Davis / E. Gorski ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance * Table 45-2 page 1280 Kidneys filter170L of plasma qd excrete only 1.5 L urine retain or eliminate electrolytes master ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Closed system of tubes that carries blood. Arteries carry blood from heart ... filtered fluid is returned to the capillary (Starling's law of the capillaries ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ... THE VITAL PUMP the heart a large organ made of cardiac muscle cells rich in mitochondria main function = to keep blood moving ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Shock in the Pediatric Patient: or Oxygen Doesn t Go Where the Blood Won t Flow! Author: Robert Pettignano Last modified by: IS&T Created Date
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 18 Renal Failure Section I . Introduction Kidneys are the principal excretive organs But also regulate a variety of material in plasma to ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view