BEM Systems Architecture 4 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 40
Title:
BEM Systems Architecture 4
Description:
Communication protocols are necessary as communication interfaces ... Pyranometer. Intelligent Buildings Technology. BEM Systems Sensors. Water Temperature ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:71
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: BEM Systems Architecture 4
1
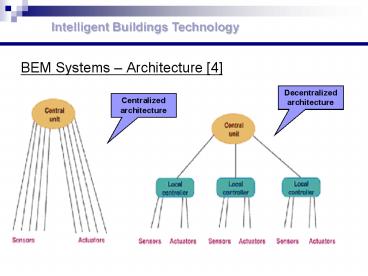
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- BEM Systems Architecture 4
Decentralized architecture
Centralized architecture
2
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- BEM Systems Architecture 5
3
BEM Systems Communication 1
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Communication protocols are necessary as
communication interfaces between the elements
that consist the systems (sensors, actuators,
controllers, etc.) - Information should be transferred and delivered
in a certain way that is defined by the
communication protocol - The compatibility of each element of the BEM
system with the communication protocol is an
essential parameter when structuring the system
4
BEM Systems Communication 2
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Network topologies determine the way the Operator
Workstation (OWS) is connected with the various
equipment - Point-to-Point The simplest approach where the
OWS is directly connected with an outstation - Star Like Point-to-Point but more than one units
are connected to OWS - Bus The various units communicate independently
between them and the OWS. The extension of the
network is simple - Ring Information is transferred around the ring
only in one direction. Each unit recognizes if
the information is of its own concern, otherwise
information bypasses the unit (token-passing
protocol) - Tree or Hierarchical Units communicate through a
tree topology
5
BEM Systems Communication 3
Intelligent Buildings Technology
6
BEM Systems Communication 4
Intelligent Buildings Technology
7
BEM Systems Communication 5
Intelligent Buildings Technology
8
BEM Systems Communication 6
Intelligent Buildings Technology
9
BEM Systems Communication 7
Intelligent Buildings Technology
10
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Measurement of solar radiation
- Temperature sensors
- Humidity sensors
- Measurement of wind velocity and direction
- Flow metering sensors
- Air pollutants measurement sensors (CO, CO2)
- Presence/Occupancy sensors
11
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
12
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
13
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
14
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
15
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
16
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
17
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
18
BEM Systems Sensors
Intelligent Buildings Technology
19
BEM Systems Actuators
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- The selection of an actuator should be based on 2
main criteria - Control strategy
- The type of equipment that will be controlled
- Reliability the power of the actuator should
respond to real operational conditions (e.g. wind
pressure on shading devices) - Time respond Should be small especially in
security systems control or error handling - In case of malfunction same control equipment
should be return to a security position - Other criteria accuracy, compatibility with the
network, life time, maintenance, calibration, etc.
20
BEM Systems Actuators
Intelligent Buildings Technology
21
BEM Systems Actuators
Intelligent Buildings Technology
22
BEM Systems Actuators
Intelligent Buildings Technology
23
BEM Systems Actuators Shading devices
Intelligent Buildings Technology
24
BEM Systems Actuators Shading devices
Intelligent Buildings Technology
25
BEM Systems Actuators Ventilation
Intelligent Buildings Technology
26
BEM Systems Actuators Ventilation
Intelligent Buildings Technology
27
BEMS Control of the System
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Open loop
- Closed loop
28
BEMS Control of the System
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- On/Off There are only 2 states of outputs (e.g.
in a valve fully opened/fully closed)
29
BEMS Control of the System
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Logic programming The implementation of the
control strategy is based on the use of logical
rules - IF (Room temperature is over 26C) THEN (Close
blinds) AND (Switch fans off) - The connected appliances are controlled mainly by
On/Off
30
BEMS Control of the System
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Fuzzy Logic This kind of control require the
synthesis of a large number of parameters and
sometimes is quite difficult to predict the
behavior of the controller - The use of fuzzy logic can be efficient for
controlling complicated parameters such as
thermal comfort
31
BEMS Control of the System
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Neural Networks The structure of these
controllers tries in a certain way to emulate the
function of the human brain - They are using mainly in non-linear systems
- The can divided in various layers. The 1st layer
is composed by the Inputs while the last by the
Outputs - A layer may includes nodes that connect this
layer with nodes in the next layer through
weighted links
32
BEMS Control of the System
Intelligent Buildings Technology
33
BEMS Control of the System
Intelligent Buildings Technology
34
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Communication
- Protocols
35
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Communication protocols
- Industrial progress in semiconductor development
and growing demands by the end user, e.g. better
control performance, have led towards advanced
control systems, known as serial networked
control network systems. Features of these
control systems are - Distributed intelligence, using microcontrollers.
- Real-time operations are possible.
- Peer-to-peer architecture.
- Memory and software programs are provided at node
level. - Software is implemented in layered protocol
stacks. - The limitations of serial networked control
systems lie mainly in network expansion, a
limited variety of topologies and transmission
media. These limitations are overcome by the new
generation of distributed control network systems
with the following features - Mixing of communications media (twisted pair,
power line, radio, infrared, fibre optics,
coaxial). - A better, or more complete, implementation of the
OSI model with higher reliability of the
(growing) network. - Free topology.
- User-friendly software and available development
tools. - Connectivity units, gateways, bridges, routers
and repeaters.
36
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Communication protocols
- With distributed control network systems a major
step towards intelligent building automation
systems has been made, resulting in - Lower operating costs
- Demands for sharing information
- Improved human environment, especially work place
conditions - Improved building performance and economy
- Similar to a factory plant, a public building
includes several types of network systems, such
as - Building automation systems responding to
external conditions and controlling the internal
environment or generating alarms. - Building management systems monitoring, managing
and storing control data. - Local area network system handling information
exchange within a company. - Communication systems providing links for
worldwide communication and data exchange.
37
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Communication protocols
- Building automation systems are used for the
following automation services and control tasks - Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC)
- Lighting and emergency lighting control
- Power management
- Security and protection
- Transport (lifts)
- These automation services are currently supported
by communication protocols such as - BACNET
- ARCNET
- BitBus
- CAN
- EIBUS
- LonWorks
- PROFIBUS
- And many other systems based on RS-232, RS-422,
or RS-485 communication standards.
38
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Communication protocols EIBUS
- Founded in 1990 by 15 firms, the European
Installation Bus (EIB) Association is now an
association of almost 100 electrical installation
firms who have joined together for the purpose of
bringing about a common standard for installation
buses in the market place. Their objective for a
uniform building management system throughout
Europe is achieved by - Laying down technical directives for systems and
products. - Devising quality rules.
- Drawing up test procedures.
- Making system know-how available to members,
subsidiaries and licensees. - Engaging test institutes to perform quality
inspections. - Granting third parties who pass tests the use of
the "EIB" mark. - Taking an active part in standardization.
39
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Communication protocols EIBUS
- EIB concentrates unequivocally on home and/or
building management. This focus permits it to
deal with all tasks and challenges within this
domain thoroughly and efficiently. The European
Installation Bus (EIB) is an open, comprehensive
system that covers all aspects of Building
Automation. - Though standardized Bus Access Unit (BAU)
building blocks are available from several
vendors. This means EIB is open EIB may be
implemented by anyone, on any chip or processor
platform chosen - both as proprietary
implementation for individual products, as well
as for OEM BAU's. Conformity tests are defined,
and EIB Certification is open to all members of
the Association. - Why "in 0th approximation"? Because EIB embeds
the protocol in an encompassing Home and Building
Electronics System, with standardized system
components (such as the BAUs), network management
and interworking standards, with a vendor-neutral
tools and programming interfaces for PC's,
training for electrical contractors,
certifications schemes etc.
40
Intelligent Buildings Technology
- Communication protocols EIBUS
- The European Installation Bus (hereafter referred
to as "the Installation Bus" or in short as "the
Bus") is designed as a management system in the
field of electrical installation for load
switching, environmental control and security,
for different types of buildings. The
Installation Bus can be installed in large
buildings such as business premises, schools,
hospitals, factories and administration premises
as well as in domestic residences. Its purpose is
to ensure the monitoring and control of functions
and processes such as lighting, window blinds,
heating, ventilation, air-conditioning, load
management, signaling, monitoring and alarms. - The EIB system allows the bus devices to draw
their power supply from the communication medium,
like Twisted Pair or Powerline (230 V mains).
Other devices may, additionally, require power
supply from the mains or other sources, as in the
Radio Frequency and Infrared media. Fig. 3.4
draws some usage examples.