Sources of Motivation PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title: Sources of Motivation
1
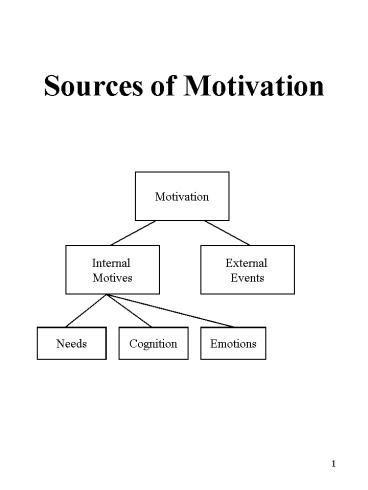
Sources of Motivation
Motivation
Internal Motives
External Events
Needs
Cognition
Emotions
2
Needs
Psychological
Physiological
Organismic
Acquired
3
Need
- - a deficiency-satisfying or growth-promoting
condition of the individual that produces energy
and behavioral direction.
4
The Need - Drive Relationship
- Needs
- Drive
- Goal-directed Behavior
5
Processes in Regulation
- Physiological Need
- Drive
- Homeostasis
- Negative Feedback
6
Processes in Regulation(cont.)
- Multiple Inputs/Multiple Outputs
- Extraorganismic Mechanisms
- Intraorganismic Mechanisms
7
Endocrine Glands
- Anterior Pituitary - controls many other
endocrine glands - Posterior Pituitary - prevents loss of water
through the kidneys - Thyroid - affects metabolic rate
- Islet Cells in Pancreas - affects utilization of
glucose - Adrenal Cortex - various effects on metabolism
sexual behavior - Adrenal Medulla - increases sugar output of liver
- Ovaries - responsible for development of sex
characteristics, but not behavior - Testes - responsible for development of sex
characteristics involved in sexual arousal
8
Thirst
- Two sources
- Osmotic Thirst - intracellular fluid depletion
- Volemic Thirst - extracellular fluid depletion
- Thirst Satiety
- Thirst the Hypothalamus
- Environmental Influences
9
Hunger
- Multiple cues
- Glucostatic Hypothesis
- Lateral Hypothalamus
- Ventromedial Hypothalamus
- Lipostatic Hypothesis
- Set-Point Theory
- The role of the Stomach
10
Hunger
- Environmental Influences
- Food variety
- Sensory cues - sight, smell, appearance, taste
- Time of day
- Stress
- Social facilitation
- Group acceptance pressure
- Restraint Release
11
Anorexia nervosa
- disorder in which preoccupation with dieting and
thinness leads to excessive weight loss - 20x more likely in females than males
- an estimated 1,000 women die each year of
anorexia nervosa. - often begins as an extension of the ritual of
normal dieting
12
Anorexia nervosa
- Danger Signs
- losing a significant amount of weight
- continuing to diet when thin
- feeling fat, even after losing weight
- fearing weight gain
- losing monthly menstrual periods
- preoccupation with food, calories, nutrition
and/or cooking - preferring to diet in isolation
- exercising compulsively
13
Anorexia nervosa
- Possible contributors
- Need for control in one's life
- Need to please others
- Dread of being fat
- Depression
- Low self esteem
- Unresolved abuse as a child
- Social attitude toward peer pressure and toward
thinness
14
Anorexia nervosa
- DSM-IV Criteria
- Refusal to maintain a normal body weight for age
and height.Maintains 85 or less of optimal
weight. - Intense fear of weight gain even though
underweight. - Disturbed self esteem affected by body weight,
size or shape - Absence of 3 or more consecutive menstrual cycles
in postmenarcheal females
15
Bulimia nervosa
- involves frequent episodes of binge eating,
almost always followed by purging and intense
feelings of guilt or shame. - Up to 5 of college women in the US are bulimic.
16
Bulimia nervosa
- Danger Signs
- binging, or eating uncontrollably
- purging by strict dieting, fasting, vigorous
exercise, vomiting or abusing laxatives or
diuretics in an attempt to lose weight - using the bathroom frequently after meals
- preoccupation with body weight
- depression or mood swings
- irregular periods
- developing dental problems, swollen
cheeks/glands, heartburn and/or bloating - experiencing personal or family problems with
drugs or alcohol
17
Obesity
- Not caused by responsiveness to external cues
- Not solely a function of how much someone eats
- Genetic forces
- Hypothalamic Signals
- Metabolic rate
- Number of fat cells
- Liver disorders
18
Obesity
- Environmental Forces
- Child-rearing practices
- Child-feeding practices
- Socio-economic status
- Fat content of diet
- Lack of exercise
- Stress
19
Obesity
- Additional Factors
- Age - metabolism slows down as people age
- Gender - males have a higher resting metabolic
rate than females - Activity level - activity tends to diminish
appetite in obese individuals - Body weight - heavier people require more
calories to maintain their body weights than
lighter one
20
Sex
- Physiological Regulation
- Hypothalamus
- controls release of androgens and estrogens
- Anterior Pituitary
- stimulated by hypothalamus to release FSH LH
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
- activates sperm production estrogen release
- Luteinizing Hormone
- activates testosterone production ovulation
21
Sex
- Four-phase
- Sexual Response Cycle
- Excitation
- Plateau
- Orgasm
- Resolution
22
Sex
- Environmental Influences
- Facial Metrics
- Neonatal features
- Sexual maturity features
- Expressive features
- Sexual Scripts
- Sexual Schemas
23
Sex
- What do men want?
- What do women want?