The Macromolecules of the Cell - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title:
The Macromolecules of the Cell
Description:
Average molecular mass = 110 daltons. The Structure and Stereochemistry ... between R ... of a Protein Containing Two Functional Domains. Domain segment. that ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:49
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Macromolecules of the Cell
1
The Macromolecules of the Cell
- Proteins
2
Proteins
- Significance of proteins
- Structural proteins
- Motility proteins
- Regulatory proteins
- Transport proteins
- Hormonal proteins
- Receptor proteins
- Defensive proteins
- Storage proteins
3
Building Blocks
4
The Structure and Stereochemistry of an Amino
Acid
5
Non-polar Amino AcidsHydrophobic
6
Polar Amino Acids Found in Proteins
7
Putting Amino Acids Together
8
Peptide Nomenclature
- Drop -ine or -ate from name and add -yl to all
amino acids in peptide. - Exceptions
- Last amino acid in peptide
- Cysteine just drop the e and add -yl
- Example Name Tyr-Ala-Cys-Gly
Tyrosyl
alanyl
cysteinyl
glycine
9
Primary (1) Structure
Phe
Leu
Trp
Lys
Met
Arg
Met
Ser
Ile
Val
Thr
Gln
N-terminus
Phe
His
Cys
Ala
Tyr
C-terminus
Polypeptide
10
Bonds and Interactions
- Covalent
- CC (peptide), SS
- 70 100 kcal/mol
- Hydrogen
- 2 - 5 kcal/mol
- Ionic
- 3 kcal/mol
- Van der Waals interactions
- 0.1 0.2 kcal/mol
- Hydrophobic interactions
11
Bonds and Interactions Involved in Protein
Folding and Stability
12
Protein Structure
- Depends on
- amino acid sequence (1o)
- Amino acid interactions (2o, 3o, 4o)
13
The Four Levels of Organization of Protein
Structure
14
The Primary Structure of Insulin
DNA sequence determines primary structure Primary
structure determines secondary, tertiary,
quaternary structures because of Bonds that are
available.
15
Secondary Structure The ? Helix and ? Sheet
16
Common Structural Motifs
17
b Pleated Sheet
antiparallel (more stable)
parallel
18
a Helices
- Collagen
http//www.glplasticandhandsurgery.com/SiteAssets/
Collagen20Closeup2.JPG
http//pbm.ct.utwente.nl/dopdrachten/yang/collagen
.gif
19
b Pleated Sheets
20
Tertiary Structure
- Determined by hydrogen bonds, SS bonds, Ionic,
and Van der Waals interactions, hydrophobic
interactions - Interactions between R groups
- Twisted, folded, coiled into native conformation
that represents most stable state for that
sequence of amino acids. - Chaperones may be involved.
21
Tertiary (3) Structure
- 3-D shape of protein
- Distant interactions
- Water is excluded from interior facilitating
interactions between R groups - Large proteins often contain domains
22
3 Structure Interactions
23
3 Structure Interactions
24
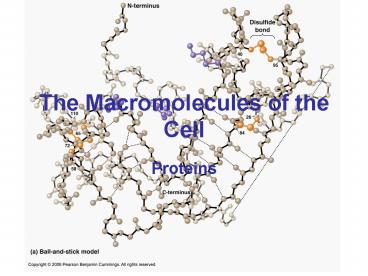
The Three-Dimensional Structure of Ribonuclease
25
The Three-Dimensional Structure of Ribonuclease
Globular Protein
Disulfide bonds stabilize tertiary structure.
26
Structures of Several Globular Proteins
27
An Example of a Protein Containing Two
Functional Domains
Domainsegment that has a specific function.
28
The Structure of Hemoglobin