Fate modelling in environmental monitoring - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
Fate modelling in environmental monitoring
Description:
[Titel] [F redragsh llare], [Datum] Use of fate models in screening ... [Titel] [F redragsh llare], [Datum] Swedish screening data in air and deposition ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:33
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Fate modelling in environmental monitoring
1
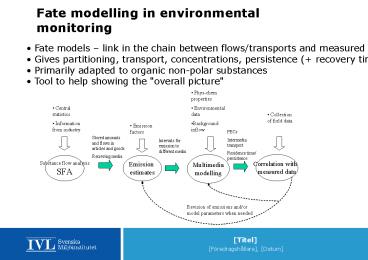
Fate modelling in environmental monitoring
- Fate models link in the chain between
flows/transports and measured levels - Gives partitioning, transport, concentrations,
persistence ( recovery time) - Primarily adapted to organic non-polar
substances - Tool to help showing the "overall picture"
2
"The overall picture"
3
Use of fate models in screening
- For the planning of sampling programmes
evaluative, generic models e.g. EQC, Level I,
II, III models - Data input phys-chem properties
- Gives knowledge on the general partitioning
properties of substances - Insight to which matrices that are most important
for sampling
4
Example of output - EQC
- Example ibuprofen
- Emissions most likely to water
- Partitioning 89 water, 11 sediment
- Conclusion Focus on water!
5
Use of fate models in screening
- For the overall picture of flows/transports
- Input Properties emission data (needs SFA or
similar) - Regional site specific model (For Nordic
purposes POPCYCLING-Baltic) - Generic models can be re-parameterised to some
extent - Screening data important for model validation
(many matrices) - Previously performed on a local scale for HBCD
- CeStoc-model (Palm, 2001 version 2Prevedouros
et al., 2007) - SFA/MFA for Stockholm performed (Palm m fl.,
2002) - Predicted levels compared to screening data
- "Overall picture" generated
6
Example - HBCD in Stockholm, results
7
Swedish screening data in air and deposition
- Evaluation of all air and deposition data
generated within the Swedish screening programme - Divided into substance groups
- Distribution of detected levels/fluxes per site
type - Assessment of LRT potential and comparison to
other measurements will be added - E.g Low levels at background sites and urban
sites, low detection frequency, low LRT potential
not prioritised - High levels at urban sites ? prioritised (risk
for exposure) - " High " levels at background sites LRT ?
prioritised
8
Screening data in air