Cytoskeleton - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 74
Title:
Cytoskeleton
Description:
4. 5. Cytoskeleton. Microtubules. Largest of cytoskeletal components ... Coding region of gene stops at terminator site which signals enzyme to release. 49 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:183
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cytoskeleton
1
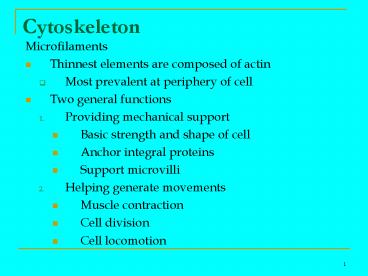
Cytoskeleton
- Microfilaments
- Thinnest elements are composed of actin
- Most prevalent at periphery of cell
- Two general functions
- Providing mechanical support
- Basic strength and shape of cell
- Anchor integral proteins
- Support microvilli
- Helping generate movements
- Muscle contraction
- Cell division
- Cell locomotion
2
(No Transcript)
3
Cytoskeleton
- Intermediate filaments
- Thicker than microfilaments but thinner than
microtubules - Several different proteins
- Exceptionally strong
- Found in parts of cells subject to mechanical
stress - Stabilize position of organelles such as nucleus
- Help attach cells to one another
4
(No Transcript)
5
Cytoskeleton
- Microtubules
- Largest of cytoskeletal components
- Long, unbranched hollow tubes
- Composed mainly of tubulin
- Assembly begins in centrosome growing outward
into cell - Help determine cell shape
- Involved in the movement of vesicles,
chromosomes, cilia, and flagella
6
(No Transcript)
7
Centrosome
- Located near the nucleus
- Consists of
- Pair of centrioles
- Cylindrical structures with nine clusters of
three microtubules arranged in circular pattern - Pericentriolar material
- Hundreds of ring-shaped complexes composed of
tubulin - Organizing centers for growth of mitotic spindle
in cell division - Replicate during cell division
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
Cilia and Flagella
- Cilia
- Numerous, short, hair like projections extending
from surface of cell - Function to move fluid along cell surface
- Flagella
- Similar in structure to cilia, but much longer
- Function to move entire cell
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
Ribosomes
- Sites of production of protein synthesis
- Contain high content of RNA
- Consists of two subunits
- Made in nucleus
- Large subunit
- Small subunit
- Some attach to endoplasmic reticulum
- Free ribosomes produce proteins used in cytosol
17
(No Transcript)
18
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Network of membranes
- Rough ER
- Continuous with nuclear envelope
- Studded with ribosomes
- Proteins synthesized here enter spaces in ER for
processing and sorting - Smooth ER
- Lacks ribosomes
- Contains unique enzymes that synthesize fatty
acids and steroids - Specialized function depending on location
19
(No Transcript)
20
Golgi Complex
- Most proteins synthesized on rough ER transported
to other regions of cell - All pass through the Golgi complex
- 3-20 cisternae
- Small flattened membranous sacs
- Two surfaces
- Entry face on rough ER surface
- Exit face on plasma membrane surface
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
Lysosomes
- Membrane enclosed vesicles
- Form from Golgi complex
- Contain as many as 60 enzymes
- Break down molecules
- Help recycle worn out cell parts
- Autophagy digestion of other organelles
- Work best in acidic pH (5)
- Membrane pumps import hydrogen ions keeping pH low
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
Peroxisomes
- Similar in structure to lysosomes but smaller
- Contain oxidases
- Enzymes that oxidize various organic substances
- Detoxifying some
- Normal metabolism for others
- One enzyme is catalase
- Decomposes toxic hydrogen peroxide into water and
oxygen gas
27
Proteasomes
- Destroy unneeded, damaged, or faulty proteins in
cell - Contain proteases
- Enzymes that break proteins into small peptides
- Leading step to recycling amino acids
28
Mitochondria
- Site of most ATP production
- Numbers vary from hundreds to thousands per cell
- Double membraned organelle
- Contains its own DNA
- Can self replicate
- Inner membrane characteristics
- Inward folds are called cristae
- Inner space called matrix
- Cellular respiration reactions occur here
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
(No Transcript)
34
Concept 3.5 Nucleus
35
Nucleus
- Usually most prominent feature of cell
- A few cells have multiple nuclei but most have
only one - Have a double membrane
- Outer membrane contiguous with rough ER
- Openings in envelope called nuclear pores
- Control movement of substances
36
Nucleus
- Contains DNA
- DNA has genes
- Genes arranged along chromosomes
- Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pair)
- Entire genetic information is called genome
- Chromosomes are DNA coiled around specialized
proteins - Uncoiled DNA with its associated proteins
(histones) and RNA is called chromatin
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
Concept 3.6 Transcription and Translation
45
Gene Expression
- DNA is the blue print for RNA
- RNA is the blue print for protein
- Proteins determine the physical and chemical
characteristics of cells - Three RNA nucleotides (codon) code for a
particular tRNA (anticodon) which carries a
particular amino acid - Therefore, the sequence of DNA nucleotides
determines sequence of RNA nucleotides which in
turn determines the sequence of amino acids
46
(No Transcript)
47
Transcription
- DNA is the blue print for RNA
- DNA stays in the nucleus, RNA is transcribed from
DNA and is mobile - mRNA strand is read by ribosomes and signal for
particular tRNAs carrying specific amino acids - RNA polymerase is the enzyme catalyzes
transcription - Promoter sequence before coding region
48
Transcription
- Base pairing
- DNA nucleotide binds to RNA nucleotide
- Adenine Uracil
- Thymine Adenine
- Guanine Cytosine
- Cytosine Guanine
- Coding region of gene stops at terminator site
which signals enzyme to release
49
(No Transcript)
50
Translation
- Nucleotide sequence is read by ribosome
- Occurs in cytosol
- Codon on mRNA signals for tRNA carrying
particular amino acid - Small subunit has binding site for mRNA
- Large subunit has two binding sites for tRNA P
site and A site. - See figure 3.26
51
(No Transcript)
52
(No Transcript)
53
(No Transcript)
54
(No Transcript)
55
(No Transcript)
56
(No Transcript)
57
(No Transcript)
58
(No Transcript)
59
Concept 3.7 Cell Division
60
Cell Division
- Cytoplasmic division called cytokinesis
- Somatic cell division
- Produces two new identical cells
- Nuclear division called mitosis
- Reproductive cell division
- Produces gametes with half as many chromosomes as
primary cell - Nuclear division two-step division called meiosis
61
Somatic Cell Division
- Cell cycle
- Sequence of events that cell undergoes until it
divides - Cells with pairs of chromosomes are diploid
symbolized 2n - One member of each pair is inherited from
biological father and the other member is
inherited from biological mother - Pair are called homologues
- Each one called homologous chromosome
62
Somatic Cell Division
- Cell cycle
- Interphase
- G1
- Cell is metabolically active replicates most
everything BUT its DNA (8-10 hours) - S phase
- Cell duplicates its DNA (8 hours)
- G2
- Growth continues
- Cell prepares for division
- Replication of centrosomes completed
- Cell now ready for mitotic phase
63
(No Transcript)
64
(No Transcript)
65
Mitotic Phase of Cell Cycle
- Nuclear division followed by cytokinesis
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
- See figure 3.30a, b, c, d, e
66
(No Transcript)
67
Cytokinesis
- Process begins during anaphase
- Formation of cleavage furrow
- When complete two new identical cells results
- See figure 3.32
68
(No Transcript)
69
(No Transcript)
70
Reproductive Cell Division
- Meiosis occurs in two rounds of cell division
- Meiosis I and meiosis II
- The goal of meiosis I is to mix (during synapsis)
and separate the homologous chromatids - Cells now haploid
- Meiosis II looks just like mitosis but with half
as many chromosomes
71
(No Transcript)
72
Meiosis versus Mitosis
- Mitosis results in two new identical cells
- Meiosis results in four cells which are all
genetically different from original starting cell
73
(No Transcript)
74
End Chapter 3