Human Endocrine System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title:
Human Endocrine System
Description:
Others affect almost all body tissues. Tropic Hormones target ... Dilate bronchioles during breathing. Epinephrine used in Asthma medications. ADRENAL CORTEX ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:104
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Human Endocrine System
1
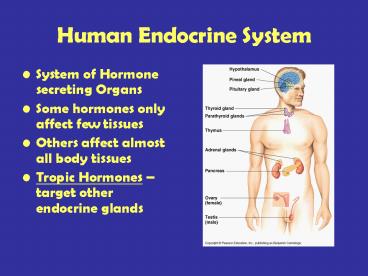
Human Endocrine System
- System of Hormone secreting Organs
- Some hormones only affect few tissues
- Others affect almost all body tissues
- Tropic Hormones target other endocrine glands
2
Table of all Glands and their Hormones
3
HYPOTHALMUS
- Integrates Endocrine and Nervous Systems
- Receives information from nerves all over body
- Releases endocrine signals appropriate to nerve
inputs - Secretions are stored in and regulate the
- Pituitary Gland
4
PITUITARY GLAND
- Master Gland
- Hormones regulate other endocrine functions
- Two Distinct regions
- Anterior Pituitary
- Posterior Pituitary
5
POSTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND
- Releases two hormones
- Oxytocin
- Induces uterus to contract during childbirth
- Releases milk during nursing
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
- Regulates osmolarity of blood
- Retention of water in kidneys
More on Posterior
6
Figure 45.6a Hormones of the hypothalamus and
pituitary glands
7
ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND
- Produces many hormones
- Growth Hormone (GH)
- Promotes growth in tissues
- Growth disorders result from abnormal GH
production - Overproduction GIGANTISM
- Underproduction - DWARFISM
More on Anterior
8
ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Stimulates activities in testes and ovaries
- Leutinizing Hormone (LH)
- Stimulates activities in testes and ovaries
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Stimulates hormone production by thyroid
- Endorphins
- Hormones that inhibit the perception of pain
- Released when pain and stress reach certain level
- Growth Hormone (GH)
- Promotes growth in tissues
- Growth disorders result from abnormal GH
production - Overproduction GIGANTISM
- Underproduction - DWARFISM
More on Anterior
9
Figure 45.6b Hormones of the hypothalamus and
pituitary glands
10
PINEAL GLAND
- Small organ near center of brain
- Secretes the hormone
- MELATONIN affects skin pigments
- Most pineal functions related to biorythms
associated with reproduction - Biological Clock
11
THYROID GLAND
- Two lobed organ located on the rear of trachea in
throat - Produces two similar hormones
- Triiodothyronine (T3) more active
- Thyroxine (T4)
- Critical in development and maturation
- Controls
- Blood Pressure
- Heart Rate
- Muscle Tone
- Digestion
- Reproduction
- Shortage of Thyroid hormone causing enlargment
- Goiter results from lack of iodine
12
Figure 45.7 Two thyroid hormones
13
Figure 45.8 Feedback control loops regulating
the secretion of thyroid hormones T3 and T4
14
PARATHYROID GLAND
- Four glands embedded in the Thyroid Gland
- Secretes
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
- Raises calcium ion levels in blood Ca 2
- Functions in processing of Vitamin D
- Works in conjunction with Thyroid and Calcitonin
in Negative Feedback System
15
Figure 45.9 Hormonal control of calcium
homeostasis in mammals
16
PANCREAS
- These clusters of cells are found throughout the
pancreas and secrete two major hormones - Islets of Langerhans
- Alpha Cells
- Secrete GLUCAGON
- Beta Cells
- Secrete INSULIN
- Regulate the amount of GLUCOSE in blood
- Two types of Diabetes exist
- Type I
- Type II
17
PANCREAS
- TYPE I Diabetes
- Autoimmune disorder.
- Usually appears in childhood.
- Treatment insulin injections.
- Type II diabetes mellitus (non-insulin-dependent
diabetes) - Usually due to target cells having a decreased
responsiveness to insulin. - Usually occurs after age 40 risk increases with
age. - Accounts for over 90 of diabetes cases.
18
Figure 45.10 Glucose homeostasis maintained by
insulin and glucagon
19
ADRENAL GLANDS
- Located adjacent to the kidneys
- 2 Regions
- Adrenal cortex - outer portion.
- Adrenal medulla - inner portion
- Adrenal Medulla reacts to stress and is closely
related to Nervous System - Adrenal Cortex also reacts to stress, but
responds to endocrine signals
Adrenal Glands and Stress
20
ADRENAL MEDULLA
- Secretes epinephrine or ADRENILINE and
noradreniline - Response to either positive or negative stress
- Responses include
- Pleasure
- Fear
- Danger
- Release of hormones directly into blood results
in rapid bioenergetic boost
MORE
21
ADRENAL MEDULLA
- Epinephrine and Noreinephrine
- Increase Glycogen breakdown in Liver and Skeletal
Muscles - Increase volume of Heartbeat
- Dilate bronchioles during breathing
- Epinephrine used in Asthma medications
22
ADRENAL CORTEX
- Stress causes HYPOTHALAMUS to release hormone
that stimulate Anterior Pituitary to release ACTH - Raises blood Glucose levels
- Key Hormones include
- Corticosteroids
- Glucocorticoids
- Mineralocorticoids
23
Figure 45.14 Stress and the adrenal gland
24
TESTES
- Synthesize these hormones
- ANDROGENS
- Main hormone
- Testosterone
- Stimulate and maintain male reproductive system
and sex characteristics - Adrogens responsible for male development as
fetus and secondary sex characteristics at
puberty - Hair Growth
- Low Voice
25
OVARIES
- Synthesize these hormones
- ESTROGENS
- Similar role in maintaining female reproductive
system and secondary sex characteristics - Secretion regulated by FSH and LH
26
Table 45.1 Major Vertebrate Endocrine Glands and
Some of Their Hormones (HypothalamusParathyroid
glands)
Second part of Table
27
Table 45.1 Major Vertebrate Endocrine Glands and
Some of Their Hormones (PancreasThymus)
28
Thymus
- Produces Thymosin which stimulates production of
lymphocytes