SQUAM System PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: SQUAM System
1
(c)
The SST Quality Monitor (SQUAM) Alexander
Ignatov1, Prasanjit Dash2 1NOAA/NESDIS/STAR
2Colorado State University-CIRA
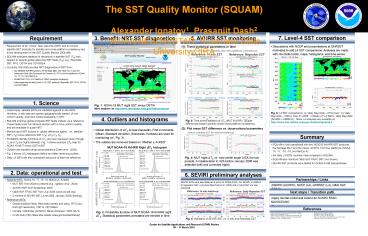
7. Level-4 SST comparison
3. Benefit NRT SST diagnostics
5. AVHRR SST monitoring
Requirement
- Requirement of an online near real-time (NRT)
tool to monitor satellite SST products for
stability and cross-platform consistency led to
the development of the SST Quality Monitor
(SQUAM). - SQUAM analyzes statistics of deviations in
satellite SST (TS) with respect to several global
reference SST fields (TR), e.g., Reynolds SST,
RTG, OSTIA and ODYSSEA. - Currently, SQUAM provides NRT diagnostics of SST
from - two NESDIS AVHRR systems the heritage Main Unit
Task (MUT) and the Advanced Clear-Sky Processor
for Oceans (ACSPO), for five platforms
NOAA-16,-17,-18,-19 MetOp-A - EUMETSAT OSI SAF MetOp-2 FRAC (analyses
underway) - Intercomparison of daily Level-4 (L4) SST
products Reynolds SST, RTG, OSTIA and ODYSSEA
- Discussions with NCEP and presentations at GHRSST
motivated to add L4 SST comparisons. Analyses are
made with Hovmöller plots, maps, histograms, and
time-series (examples given below)
(1) Trend statistical parameters in time
(check satellite SST stability and cross-platform
consistency)
Reference In situ SST
Reference Reynolds SST
Median Bias
(b)
Robust Standard Dev.
Cross-platform consistency (using
double-differencing technique)
1. Science
(c)
(a)
Fig. 1 NOAA-19 MUT night SST minus OSTIA. More
analyses at http//www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/sod/s
st/squam/
Cross-consistency
- Customarily, satellite SSTs are validated against
in situ SSTs. However, in situ data are sparse,
geographically biased, of non-uniform quality,
and have limited availability in NRT. - SQUAM employs global analyses SST fields instead,
as a reference. These fields cover full retrieval
domain with a more uniform quality, and are
available in quasi-NRT. - Monitoring of SST is done in global difference
space, i.e., satellite SST (TS) minus reference
SST (TR), ?TSTS-TR. - Probability density functions of ?TS are
near-Gaussian (even though TS and TR are highly
skewed). Fig. 1 shows example ?TS map for NOAA-19
MUT minus OSTIA SST. - Outliers are handled using robust statistics
(Dash et al., 2009). - Fig. 2 shows ?TS histograms before and after
removing outliers. - Daily L4 SSTs are also compared using one of them
as reference.
Fig. 6 L4 SST comparisons. a) daily Reynolds
RTG (low), b) daily Reynolds OSTIA,
Dec-31-2009, c) Mean of L4 SSTs - daily
Reynolds (AVHRR AMSR-E). More L4 analyses are
available at http//www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/sod/
sst/squam/L4
4. Outliers and histograms
Fig. 3 Time-series statistics of ?TS (MUT
AVHRR). Double-differences (bottom panels) check
cross-platform consistency.
- Global distribution of ?TS is near-Gaussian.
First 4 moments (Mean, Standard deviation,
Skewness, Kurtosis) are used for monitoring (cf.,
Fig. 3). - The outliers are removed based on Median
4RSD criterion.
(2) Plot mean SST difference vs. observational
parameters (check satellite SST for
self-consistency)
Summary
- SQUAM is fully operational with two NESDIS AVHRR
SST products, the heritage MUT and the newer
ACSPO, from five platforms (NOAA-16, -17, -18,
-19, and MetOp-A). - Six daily L4 SSTs routinely intercompared in
SQUAM. - SQUAM also monitors OSI SAF FRAC SST (not
shown). - SEVIRI SST products were tested for GOES-R ABI
preparedness.
MUT NOAA-18 AVHRR Night ?TS histogram
Fig. 4 MUT night ?TS vs. view zenith angle (VZA)
for two periods. A misallocation in VZA before
January 2006 was detected (left) and corrected
(right).
AVHRR SST in situ
2. Data operational and test
6. SEVIRI preliminary analyses
Partnerships / Links
Before outlier removal
After outlier removal
- Satellite SSTs NOAA-16, 17, 18, 19, MetOp-A,
MSG - MUT SST from 2004 to present (e.g., Ignatov et
al., 2004) - ACSPO SST from September 2008
- OSI SAF FRAC SST from July 2008
(www.osi-saf.org) - 2 months of SEVIRI SST (June 2008, January 2009)
testing - Reference SSTs
- Global analysis fields Reynolds (weekly and
daily), RTG (low and high resolution), OSTIA,
ODYSSEA - Climate Pathfinder (ACSPO), Bauer-Robinson 1985
(MUT) - In situ bulk (http//www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/sod/
sst/calval/)
SEVIRI SSTs were also tested as a proxy for
GOES-R ABI. For SEVIRI, in addition to regression
SST, a physical (Merchant et al., 2009) and a
hybrid SST are also produced.
- OSDPD (ACSPO), NCEP (L4), GHRSST (L4), OSI SAF
(FRAC)
Next steps / Transition path
Reference In situ match-up
Reference Daily Reynolds SST
AVHRR SST OSTIA
- Apply diurnal model and extend for ACSPO FRAC,
NAVOCEANO - Transition path not foreseen web-based system
quasi-operational
Mean Bias (K)
References
Fig. 2 Probability function of MUT NOAA-18 AVHRR
night ?TS. Statistical parameters annotated are
trended in time.
Std. Dev. (K)
- Autret Piollé, 2007 ODYSSEA User manual,
CERSAT IFREMER - Dash et al., 2009 submitted to J.Tech.
- Gemmill et al., 2007 RTG-HR. NOAA/NWS/NCEP/MMAB
260, 39pp - Ignatov et al., 2004 13th AMS Conf., Norfolk,
VA, 20-24 Sep., 2004 - Kilpatrick et al., 2001 JGR, 106, 9179-9198
- Merchant et al., 2009 RSE, 113, 445-457
- Reynolds et al., 2002 JClim, 15, 1609-1625
- Reynolds et al., 2007 JClim, 20, 5473-5496
- Stark et al., 2007 OSTIA.Oceans 07IEEE, 18-22
June 2007, Scotland - Thiébaux et al., 2003 RTG-R. BAMS, 84, 645-656
Fig. 5 Validation of SEVIRI SST vs. in situ and
Reynolds SST.