- PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 7
Title:
1
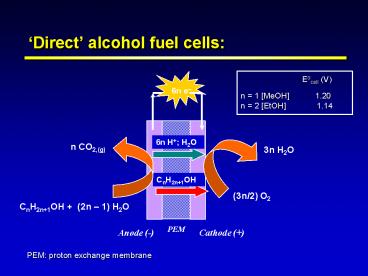
Direct alcohol fuel cells
Eocell (V) n 1 MeOH
1.20 n 2 EtOH 1.14
6n e
6n H H2O
n CO2,(g)
3n H2O
CnH2n1OH
(3n/2) O2
CnH2n1OH (2n 1) H2O
PEM
Anode (-)
Cathode ()
PEM proton exchange membrane
2
Direct borohydride fuel cell
8e-
Eocell (V) 1.64
NaBO2 6H2O
8 Na H2O
4H2,(g)
H2O
8NaOH
NaBH4 2H2O
2O2
NaBH4 8NaOH
PEM
Anode (-)
Cathode ()
PEM proton exchange membrane
3
Highlights of direct fuel cells
- Advantages
- Ethanol and methanol are primary liquid fuels
obtainable from renewable, agricultural,
resources sustainable energy - Canada is a leader in both ethanol (240 million
liters annually from agricultural resources) and
methanol production (Methanex) - The borohydride fuel cell (DBFC) is a zero-carbon
emission power source - Higher theoretical energy densities compared to
H2 H2-O2 fuel cell 550 kWh m-3H2
(at 200 atm, 293 K) - DMFC 4,800 kWh m-3 CH3OH
- DEFC 6,300 kWh m-3 C2H5OH
- DBFC 2,000 kWh m-3 (20 wt NaBH4 in 2 M NaOH)
4
Disadvantages Problems to be solved
- Poor anode performance
- Sluggish fuel electro-oxidation kinetics /
electrocatalysis - CH3OH oxidation Pt-Ru
- C2H5OH oxidation Pt-Sn
- NaBH4 oxidation Au, Pt, Metal-Hydrides
- Effect of catalyst composition, operating
conditions - Low catalyst layer utilization efficiency
- Catalyst preparation method particle size
dispersion on and interaction with
various supports ionomer network /
catalyst interface - Two-phase flow in the porous anode
- For alcohol fuel cells CO2 disengagement from
the catalyst layer mass transfer
overpotential and effective ionic conductivity - Fuel crossover from the anode to the cathode
- Membrane permeable to alcohols mixed
potential on the cathode
5
Research strategy
Surface analytical studies
- surface area, composition etc.
Cell Design variables
Colloidal precursor method
Nano-scale electrocatalyst synthesis and
deposition on substrates
Liquid crystal templated /surfactant assisted
electrodep.
Evaluation of electro-catalytic activity
Fuel cell testing and optimization
Electrochemical methods Voltammetry, impedance,
chrono-techniques
Electrodeposition from microemulsions and
micellar media
Operating conditions
6
Typical gas diffusion anode structure for direct
fuel cellsMight not be the best engineering
solution we are looking at alternatives
5 25 ?m
CO2,(g)
H2O
H H2O R-OH
C A T H O D E
NaBO2, H2,(g)
CH3OH, C2H5OH
O2
Na H2O BH4-
NaBH4
Carbon fiber diffusion layer
Catalyst layer
Ionomer (e.g. proton exchange membrane)
7
Acknowledgement
- NSERC
- Discovery Grant
- Equipment Grant
- BC ASI
- Provincial Research Fellow
- WED / CFI
- Auto 21
- Industrial collaborations
- Consultant for Vizon Sci Tech. (2002-2003)
- Colgate-Palmolive USA (2005)
- Tekion (2006-2007)