Phagocyte PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Phagocyte
1
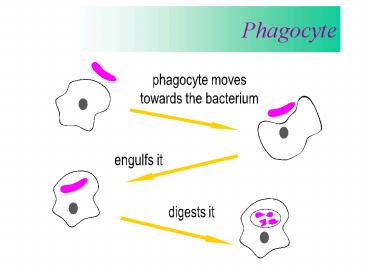
Phagocyte
phagocyte moves towards the bacterium
engulfs it
digests it
2
B cells
Receptor
B Cell
Naïve B cell
3
B cells and antibodies
B cell attaches to antigen cloning of daughter
cells
daughter cells produce antibodies
Antibodies neutralise antibodies
phagocyte consumes an antibody coated virus
4
Cytotoxic CD8 cells
CD8 cells can recognise markers on the outside of
infected cells
CD8 destroys infected cell which stops cell from
producing more virus or bacteria
5
Antigen presenting cells
These cells can engulf invading organisms
Antigens presented to CD4 cells
The foreign organism is broken up into smaller
pieces
6
CD4 cell
7
Analogy for the immune system
8
Naïve and Memory B cells
- Naïve B cell
- Once activated it divides many times making two
types of clones - The plasma cell which makes and releases large
amounts of the appropriate antibody - The memory B cell which can live for years
- Memory B cells
- The existence of memory B cells means that the
body can respond much more quickly
9
CD4 and CD8
- Cluster of Differentiation
- Molecules on the surface of the cells that help
the T cell attach to the antigen - CD4 cells
- Th1 (humoral response) Th2 (cell mediated
response) Th0 (??) - CD8 cells
- Cytotoxic lymphocytes (CTL)
- CD45RA Naïve cells
- CD45RO Memory cells
10
CD4 count viral load over time
11
HIV virion
Fatty (lipid bilayer) membrane
Glycoprotein gp120
Protein p18
Reverse transcriptase enzyme
Protein p24
12
Vaccine - Ideal characteristics
- Prevent transmission by mucosa injecting
- Excellent safety profile
- Single dose administration
- Offers protection for a long time
- Low cost
- Stability and ease of administration
- Works against a wide range of different strains
13
Immune system responses
- Humoral response
- Based on antibodies and the B cells that produce
them - Cell-mediated response
- Based on cytotoxic CD8 cells
- Mucosal immunity
- The above but concentrated in the mucosal
membranes where most transmission occurs - Current trend
- is to aim to stimulate a sufficient HIV-specific
CTL response to control or prevent HIV infection
14
Types of vaccine
- Live attenuated vaccines
- Defective or weakened form of the virus
- Previous example original smallpox vaccine,
vaccinia - Research in monkeys indicates may slowly lead to
immune disease - Inactivated or 'killed' vaccines
- Recombinant sub-unit envelope vaccines
- Recombinant vectored vaccines
- DNA vaccines and replicons
- Combination vaccines or prime and boost
15
Types of vaccine
- Live attenuated vaccines
- Inactivated or 'killed' vaccines
- Second classic technique (e.g. Dr Jonas Salk in
creating the world's first successful polio
vaccine) - No-one has yet claimed any significant success
- Maybe difficult to distinguish between vaccine
immune response and infection - Recombinant sub-unit envelope vaccines
- Recombinant vectored vaccines
- DNA vaccines and replicons
- Combination vaccines or prime and boost
16
Types of vaccine
- Live attenuated vaccines
- Inactivated or 'killed' vaccines
- Recombinant sub-unit envelope vaccines
- Seek to stimulate antibodies to HIV by mimicking
proteins on the surface of HIV (e.g. gp120) - Initial research was strain-specific and produced
poor antibody responses - Recently more hope
- Recombinant vectored vaccines
- DNA vaccines and replicons
- Combination vaccines or prime and boost
17
Types of vaccine
- Live attenuated vaccines
- Inactivated or 'killed' vaccines
- Recombinant sub-unit envelope vaccines
- Recombinant vectored vaccines
- incorporate harmless bits of HIV into established
vaccines - ALVAC series of vaccines are canarypox based
vaccines - Vaccine strains of adenovirus
- recombinant rabies virus vaccines
- DNA vaccines and replicons
- Combination vaccines or prime and boost
18
Types of vaccine
- Live attenuated vaccines
- Inactivated or 'killed' vaccines
- Recombinant sub-unit envelope vaccines
- Recombinant vectored vaccines
- DNA vaccines and replicons
- involve HIV genetic sequences which, once
injected, induce expression of HIV antigens by
human cells. - In the case of replicons, these sequences are
wrapped in the outer coat of an unrelated virus. - Combination vaccines or prime and boost