BC basic - from big bang - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
BC basic - from big bang
Description:
Chemical properties The atomic composition of living organism is more complex than others Periodical Table H C N O Life prefers lighter atoms Atomic sizes – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:57
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: BC basic - from big bang
1
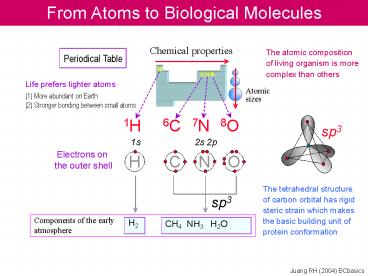
From Atoms to Biological Molecules
Chemical properties
The atomic composition of living organism is
more complex than others
H
C N O
Life prefers lighter atoms
Atomic sizes
(1) More abundant on Earth (2) Stronger bonding
between small atoms
1H
6C
7N
8O
sp3
1s
2s 2p
Electrons on the outer shell
The tetrahedral structure of carbon orbital has
rigid steric strain which makes the basic
building unit of protein conformation
sp3
Juang RH (2004) BCbasics
2
Review the structure of water
C-C
Organic compound
Electro-negativity O 3.5 N 3.0 C 2.5 H 2.1
Functional group
Permanent dipole
If atoms in a functional group have notable
difference in electronegativity, then this
functional group will express high polarity and
will be highly active
? High polarity ? High dielectric constant ?
H-bond formation ? pH influence
Juang RH (2004) BCbasics
3
Exaggerated Model for Water Molecule
sp3
-
Adapted from Zubay (1988) Biochemistry (2e) p.57
4
Dielectric Constant
Water 80.4 Methanol 33.6 Ethanol 24.3 Amm
onia 17.3 Acetic acid 6.15 Chloroform
4.81 Ethyl ether 4.43 Benzene
2.28 Carbon tetrachloride 2.24
Molecules with asymmetrical distribution of
electronegativity have higher polarity
Adapted from Bohinski (1987) Modern Concepts in
Biochemistry (5e) p.37
5
Ionic Bond Is Not Stable in Water Solution
-
Solvation
-
-
-
-
-
Adapted from Nelson Cox (2000) Lehninger
Principles of Biochemistry (3e) p.87
-
-
?
Adapted from Alberts et al (2002) Molecular
Biology of the Cell (4e) p.115
-
? But enzyme forms stable binding with its
substrate in water
6
Bond Energy in Water Might Be Different
Bond length In vacuum Water solution
0.15 nm 0.25 nm 0.30 nm 0.35 nm
90 3 1 0.1
Covalent bond Ionic bond Hydrogen bond Van der
Waal force
90 80 4 0.1
kcal/mole
Adapted from Alberts et al (2002) Molecular
Biology of the Cell (4e) p.57
7
Hydrogen Bond (H-Bond)
The linearity is important for a perfect H-bond
Weaker H-bond
Adapted from Alberts et al (2002) Molecular
Biology of the Cell (4e) p.58
8
Affinity between Two Molecules
Like Dissolves Like
Molecules having similar polarity will attract
each other
Polar ? Polar Nonpolar ? Nonpolar
Juang RH (2004) BCbasics
9
Energy of Chemical Bonds in Cells
Adapted from Alberts et al (2002) Molecular
Biology of the Cell (4e) p.53
kcal/mole
Secondary bond
Van der Waal force
0.1 kcal/mole
Hydrophobic bond
1 kcal/mole
Hydrogen bond
1 kcal/mole
Ionic bond
3 kcal/mole
Covalent bond
90 kcal/mole
Juang RH (2004) BCbasics
10
Secondary Bonds Contribute to Molecular Affinity
x
Reversible non-covalent binding
Adapted from Alberts et al (2002) Molecular
Biology of the Cell (4e) p.161