Eye Anatomy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Eye Anatomy
Description:
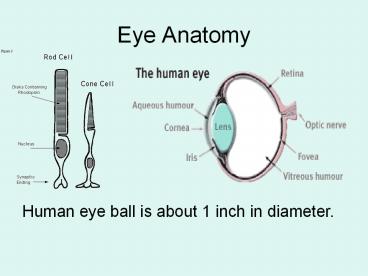
Eye Anatomy Human eye ball is about 1 inch in diameter. Eye Parts Cornea: Transparent, dome shaped; covers iris & pupil Refractive (bends light); very sensitive. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:307
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Eye Anatomy
1
Eye Anatomy
Human eye ball is about 1 inch in diameter.
2
(No Transcript)
3
Eye Parts
- Cornea
- Transparent, dome shaped covers iris pupil
- Refractive (bends light) very sensitive.
- Should be smooth
- Astigmatism if not smooth
- Light goes through the cornea first
4
Eye Parts
- Iris
- Colored part of eye surrounding pupil
- A muscle that can shrink or grow depending on the
amount of light present
5
Eye Parts
- Pupil
- The space in the center of the iris
- Just a spaceshrinks or grows depending on the
muscles of the iris - Looks like a black dot
- Indicates amount of light present
- Indicates health
6
Eye Parts
- Lens
- Transparent
- Refracts (bends light)
- Can change shape to focus (muscles on top and
bottom) - Can be replaced with a working lens if diseased
7
Eye Parts
- Retina
- Takes up 2/3 of the inside back surface of the
eye ball - Contains rod and cone nerve cells- Rods help see
light and dark- Cones help see colors - Image falls on retina (inverted and smaller)
- Tears (rips) can be fixed with lasers
8
Eye Parts
- Optic Nerve
- Connects the eye to the brain
- Blind spot is place where optic nerve is
connected to the eye ball.
9
Try these
- Blind spot
- Light bulb
- Optical illusions
- http//www.exploratorium.edu/learning_studio/cow_e
ye/step01.html
10
Common vision problems
Nearsightedness (myopia) This problem is often
discovered in school-age children who report
having trouble seeing the board.
Near-sightedness usually becomes progressively
worse through adolescence and stabilizes in early
adulthood. It is an inherited problem.
11
Nearsightedness
12
How to correct nearsightedness
- If the image needs to be stretched out to reach
the correct point on the retina, which kind of
lens is needed to correct this?
13
Common vision problems
Farsightedness (hyperopia) This vision problem
occurs when light rays entering the eye focus
behind the retina, rather than directly on it.
The eyeball of a farsighted person is shorter
than normal. Many children are born with
hyperopia, and some of them "outgrow" it as the
eyeball lengthens with normal growth.
14
Farsightedness
People who are farsighted have need to move
printed matter farther from them in order to
focus it. Usually occurs in middle age age 40.
15
How to correct hyperopia
- If the image needs to be shrunk to reach the
correct point on the retina, which kind of lens
is needed to correct this?