Understanding How a Skeletal Muscle Contracts PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title: Understanding How a Skeletal Muscle Contracts
1
Understanding How a Skeletal Muscle Contracts
2
A skeletal muscles contraction begins at the
neuromuscular junction.
- What do you think the definition of
neuromuscular junction would be?
3
Neuromuscular Junction
4
Neuromuscular junction animation
- animation
Focus Questions What is the name of the stimulus
that travels down the axon to the muscle
fiber? An action potential Does the terminal
(end) of the axon enter the muscle fiber? No.
There is a gap between the two. Does
acetylcholine enter the muscle fiber? No. What
chemical does enter the muscle fiber, resulting
in an action potential through the muscle
fiber? Sodium
5
Sliding Filament theory
- Boat Myosin (thick filament)
- Oar Myosin side arm
- Water Actin (thin filament)
- Life ring Calcium
6
Resting
- ATP is bound to myosin side arm.
- ATP cleaves into ADP P (high energy)
7
Step 1 Action potential
- A nerve action potential releases acetylcholine
into the synaptic cleft opening the Na channels. - Action potential spreads across sarcolemma
releasing Ca into sarcoplasma
8
Step 2 Myosin-actin binding
- Ca binds to troponin.
- A shape change in troponin moves tropomyocin out
of the way of actin binding site. - Actin and myosin bind using energy from cleaved
ATP.
9
Step 3 Power Stroke
- Side arm pivots so myosin and actin slide by each
other shortening the sarcomere. - ADP and P released (low energy)
10
Step 4 ATP BindingActin-myosin release
- A different ATP molecule binds to active site.
- Actin released
11
Step 5 ATP cleavage
- Return to high energy state
- Cycle will repeat if Ca still available.
12
Think it over
- The boat (myosin) does not move far in one cycle,
can a muscle contraction occur with one cycle? - No
- If a muscle is contracted what happens if a new
molecule of ATP is not available? - Muscle stays contracted- cramps
- Why does rigor mortis occur? (Hint What
chemical is no longer available to the body?) - ATP is not available to control Ca release so
contractions are continuous 6-8 hours after
death. Body relaxes 16-24 hours as enzymes break
down contractile structures.
13
Sarcomere summary
14
Sliding Filament Theory
- Focus questions
- What happens to the length of the sarcomere
during a contraction? - The sarcomere shortens.
15
Sliding Filament Animation
- animation 2
- Focus Questions
- What chemical exposes the binding site for actin
and myosin? - Ca
- What is the source of energy for a contraction?
- ATP
- What is the name of the step in which the actin
filament is actively contracted? - Powerstroke
- What chemical must be present in order for the
actin and myosin filaments to separate? - ATP
16
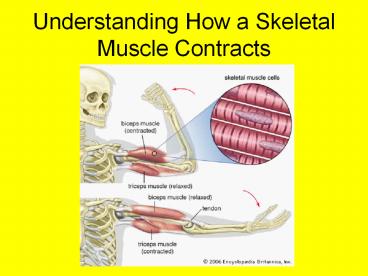
Muscle contraction at the macroscopic level
- Place your fingers along the angle of your jaw
just in front of your ear. Grit your teeth and
fell what happens to the hardness of the masseter
muscle. - During muscle contraction the muscle becomes
________________________.
17
- With your thumb and little finger of one hand,
span the opposite arms biceps from the elbow to
as close to the shoulder as possible. Bend the
arm and observe the change in the length of the
muscle. - During muscle contraction the muscle
___________________ in length.
18
- Wrap a string around your extended upper arm and
determine the circumference. - Clench your fist tightly and flex your arm
to contract the muscle. - During muscle contraction the diameter of the
muscle _____________________.