Islam-Submission to Allah - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Islam-Submission to Allah
Description:
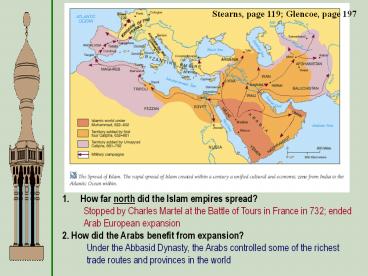
Stearns, page 119; Glencoe, page 197 How far north did the Islam empires spread? 2. How did the Arabs benefit from expansion? Stopped by Charles Martel at the Battle ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:151
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Islam-Submission to Allah
1
Stearns, page 119 Glencoe, page 197
- How far north did the Islam empires spread?
- 2. How did the Arabs benefit from expansion?
Stopped by Charles Martel at the Battle of Tours
in France in 732 ended Arab European expansion
Under the Abbasid Dynasty, the Arabs controlled
some of the richest trade routes and provinces in
the world
2
The Crusades
- In the 7th Century. Muslims, conquered Palestine
- where Jesus Christ had lived and preached
- Muslims were tolerant
- let Christians/Jews and keep their faiths
- Christian pilgrims visited the Christian 'Holy
Land shrines freely - In the 11th century, the Seljuk Turks conquered
Jerusalem - Persecuted Christian pilgrims
- 1071, defeated the Byzantine army at the Battle
of Manzikert Threatened Byzantine Empire
Emperor Alexius asked the Pope for help - Pope Urban II called for a Holy War or
Crusade against the Muslim infidels
(unbelievers) and occupiers of the Holy Lands - 1000s responded and pinned crosses on their tunics
3
The Crusades continued
- Between 1096-1212, there were 7 crusades
- 1000s responded and pinned crosses on their
tunics marched to fight/die for God - 1st Crusade (1096-1099)
- French, German, and Italian armies captured
Jerusalem - Sacked the city, slaughtered many Muslims
Jews stole/ransacked goods - Many Crusaders went home--left surrounding
territories vulnerable - Muslim leader, Saladin captured Edessa
- 2nd Crusade (1147-1149)
- 2nd Crusade failed to win Edessa back
- Additionally, Saladin re-captured Jerusalem in
1187 for the Muslims
4
The Crusades continued
- 3rd Crusade (1189-1192)
- Emperor Frederick Barbarossa of Germany drowned
in a local river - English King Richard French King Philip II of
France arrived by sea - captured the coastal cities
- unable to move inland capture Jerusalem
- Saladin was impressed with King Richards
fighting on the coast - King Richard earned the nickname the
Lionhearted here - Saladin agreed to allow Christian pilgrims free
access to Jerusalem
5
- Muslim leader
- Established the Ayyubid Dynasty
- Very devout
- Legendary chivalry
- Defeated Europeans in the 2nd 3rd Crusades
- Spared Jerusalem
- Made Cairo a vibrant medieval city
Saladin (1138-1193)
6
The Crusades continued
- 4th Crusade (1202-1204)
- Venetian leaders used the opportunity to weaken
their largest economic competitor - Diverted Crusaders to Constantinople sacked the
city and ruled it until 1261 - Byzantine army recaptured Constantinople in 1261
- Byzantine Empire never regained their great
power - Constantinople was conquered by the Ottoman
Empire in 1453
7
What was the main effect of the Crusades?
8
- Italian port cities prospered economically
- Opened Europeans to a variety of goods and
products silks, spices, coffee, tea, science,
and knowledge - Access to the compass/astrolabe provided
Europeans with the means to travel away from the
coastline and to seek new goods - Access to information about gun powder will
enhance their more aggression and lead to
imperialistic tendencies in Asia, Africa, and
the Americas - 4th Crusade sacked Constantinople
- weakened the Byzantine Empire
- Led to Anti-Semitism in Europe
- Broke down feudalism
- Paved the way for the development of
European nation-states - Lasting impact bred centuries of distrust
enmity between Muslims Christians
9
Islam the Mongols
10
Mongols
- 1258, Mongols seized Persia and Mesopotamia
- Ended Abbasid Caliphate
- Hulegu sacked Baghdad
- Destroyed libraries, mosques, palaces
Hulegu (hoo-LAY-goo)
11
- Turkish slave-soldiers (Mamluks) stopped the
Mongols at the Red Sea - Mongolians inter-married with local peoples
- Mongolians converted to Islam and spread the
religion throughout Asia/southern Europe - Mongolian conquest ended Baghdads leadership
- Cairo became the new center of Islamic
civilization
12
(No Transcript)
13
Baghdad
- New capital
- Ideal location
- Close to Persian capital
- Spectacular city
- Economic center of Muslim world
- Banking checks
- Academic center
14
Islam - Widespread
- Urban expansion
- Long-distance trade
- Increase in handicraft production
- New converts
15
Courtly Excesses
- Untouchable rulers
- The Shadow of God on earth
- Taste for luxury
- Caliph Harun al-Rashid 786-809
- Golden Age of Muslims
- Learning, trade, and government
16
Imperial Breakdown
- Civil war over successors with Rashids death
- Political divisions
- Shiite revolts and assassination attempts
- Slave mercenaries
- Taxes, famine, flood, bandit gangs
17
(No Transcript)
18
Islamic Achievements
- Ibn- Rushd translated Aristotles works
- Spread the Indian system with 0 easier to us
than Roman numerals - Europeans mislabeled the system Arabic
- Developed Algebra
19
Baghdad Observatory
- Knew the Earth was round
- Astrolabe helped sailors calculate the angles
of the sun and the stars. - Armillary Astronomers lined up the top rings
of the sphere and calculated the time of day or
year. This was useful for mapmaking and
calendars.
Medicine
- Ibn Sina - wrote medical encyclopedia
- The University medical textbook
- Al Qasims drawings of medical tools was the
foremost text on surgery in Europe for nearly 500
years
20
Literature
Ibn Khaldun (14th C) -
Muslim historian - Civilizations
rise/decay in cycles
Omar Khayyam (12th C) - Rubiyat
- Arabian Nights
21
Architecture
Mosque in Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Mosque of Cordova, Spain Center of learning
culture
22
Art writing
Calligraphy
Arabesques
23
Arab dhow with lateen sails
24
Ibn Battuta
1304-1349?
- Most celebrated Muslim traveler in the
postclassical world - Islamic scholar who recorded his travels
throughout the dar al Islam (Muslim states) - Traveled over 75,000 miles to Spain, Timbuktu,
China, India, the Maldives Islands, East Africa,
and the Mali Empire - Worked in government positions everywhere he
went as an adviser or judge - Promoted the proper observance of Islam
25
(No Transcript)
26
Key Terms
Shari'ah The revealed and the canonical laws
of the religion of Islam. The legislative power
in the government lies in the hands of
legislative assembly. The legislators are to make
rules and regulations within the scope and
dimensions of the Qur'an and the Sunnah of the
Prophet. These rules constitute the
Shari'ah. Mosque Muslim building of prayer and
worship. Jihad Literally means, "struggle or
striving refers to the obligation of all
Muslims to struggle against error and evil. In
another sense it refers to the defensive military
struggle against those who would attack Muslims
and subvert their faith, hence the concept of the
'Holy war. P.B.U.H. These letters are
abbreviations for the words Peace Be Upon Him
which corresponds to the meaning of the Arabic
expression Alaihis Salam, which is an
expression that is said when the name of a
prophet is mentioned. This expression is widely
used by English speaking Muslims. It is to be
noticed here that this expression does not give
the full meaning of "Salla Allahu 'Alaihi Wa
Sallam (may the blessing and the peace of Allah
be upon him). Therefore it is recommended that
people do not use (p.b.u.h.) after the name of
prophet Muhammad (s.a.w.) they should use "Salla
Allahu 'Alaihi Wa Sallam" instead, or they may
use the abbreviated form of (s.a.w) in writing.
27
- Comparisons Holy men in Islam, Christianity, and
Buddhism - Read page 13.
- Make a Venn diagram comparing the role of holy
mystics in the 3 religions
28
Perspectives Gender Roles in Early Islamic
Societies 1. Read page 15. 2. Describe the
similarities and differences in gender roles in
Muhammads era, the Umayyad dynasty, and the
Abbasid dynasty. 3. Give specific similarities
and differences between all 3. 4. Give specific
details/evidence to support your similarities and
differences.
29
Abbasid Empire
Pre-Islamic
- Under influence of Persian culture, women veiled
and secluded - Increase in patriarchal authority
- Only males permitted multiple marriages
- Development of the harem
- Lower class women enjoyed more freedom than
upper class women
Similarities
- - Had greater liberty than those of Byzantium or
Persia - Played important economic roles
- Matrilineal descent in some clans
- Not secluded
- Both males and females allowed multiple marriages
in some clans - Women often fought beside men
- Patriarchal
- More urbane, the less freedom women have