Nervous Systems PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 46
Title: Nervous Systems
1
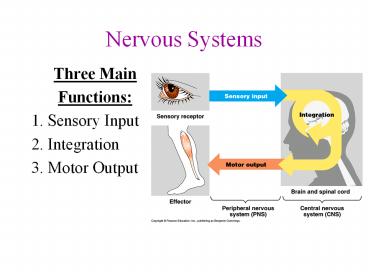
Nervous Systems
- Three Main
- Functions
- 1. Sensory Input
- 2. Integration
- 3. Motor Output
2
Two Main Parts of Vertebrate Nervous Systems
- Central nervous system (CNS)
- brain and spinal cord
- integration
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- network of nerves extending into different parts
of the body - carries sensory input to the CNS and motor output
away from the CNS
3
Two Cell Types in Nervous Systems
- Neurons
- Cells that conduct
- the nerve impulses
- Supporting Cells
- Neuroglia
4
Figure 48.2x Neurons
5
Three Major Types of Nerve Cells
- Sensory neurons
- communicate info about the external or internal
environment to the CNS - Interneurons
- integrate sensory input and motor output
- makes synapses only with other neurons
- Motor neurons
- convey impulses from the CNS to effector cells
6
(No Transcript)
7
Supporting Cells - Neuroglia
- provide neurons with nutrients, remove wastes
- Two important types in vertebrates
- Oligodendrocytes myelin sheath in CNS
- Schwann cells -myelin sheath in PNS
8
Myelin Sheath Formation
9
(No Transcript)
10
Conduction of the Nerve Impulse
- Membrane Potential
- Voltage measured across a membrane due to
differences in electrical charge - Inside of cell is negative wrt outside
- Resting potential of neuron -70 mV
11
Figure 48.6 Measuring membrane potentials
12
(No Transcript)
13
Sodium-Potassium Pump
14
Excitable Cells
- Neurons muscle cells
- Have gated ion channels that allow cell to change
its membrane potential in response to stimuli
15
(No Transcript)
16
Gated Ion Channels
- Some stimuli open K channels
- K leaves cell
- Membrane potential more negative
- hyperpolarization
- Some stimuli open Na channels
- Na enters cell
- Membrane potential less negative
- depolarization
17
Gated Ion Channels
- Strength of stimuli determines how many ion
channels open - graded response
18
Nerve Impulse Transmission
19
Action Potentials
- Occur once a threshold of depolarization is
reached - -50 to 55 mV
- All or none response (not graded)
- Magnitude of action potential is independent of
strength of depolarizing stimuli - Hyperpolarization makes them less likely
20
(No Transcript)
21
Refractory Period
- During undershoot the membrane is less likely to
depolarize - Keeps the action potential moving in one direction
22
Propagation of Action Potential
- Action potential are very localized events
- DO NOT travel down membrane
- Are generated anew in a sequence along the neuron
23
(No Transcript)
24
Saltatory Conduction
25
Transfer of Nerve Impulse to Next Cell
- Synapse
- the gap between the synaptic terminals of an axon
and a target cell
26
Transfer of Nerve Impulse to Next Cell
- Electrical synapses
- Gap junctions allow ion currents to continue
- Chemical synapses
- More common
- Electrical impulses must be changed to a chemical
signal that crosses the synapse
27
Synapses
28
Neurotransmitters
29
Effects of Cocaine
30
(No Transcript)
31
Integration of multiple synaptic inputs
32
Summation of postsynaptic potentials
33
Diversity of Nervous Systems
34
CNS
Brain and Spinal Cord
Motor Pathways
Sensory Pathways
Sensory neurons registering external stimuli
Sensory neurons registering external stimuli
PNS
Somatic nervous system (voluntary)
Autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
Sympathetic nervous system "fight or flight"
Parasympathetic nervous system "rest and repose"
central nervous system (CNS)
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
Vertebrate Central Nervous System
- Spinal Cord
- Receives info from skin muscles
- Sends out motor commands for movement response
- Brain
- More complex integration
- Homeostasis, perception, movement, emotion,
learning
38
Vertebrate Central Nervous System
- White matter
- Internal part of brain external part of spinal
cord - Myelinated axons
- Gray matter
- Cell bodies of neurons
39
Figure 48.16x Spinal cord
40
Vertebrate Central Nervous System
- Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Fills central canal of spinal cord and ventricles
of brain - Shock absorption
41
Functions of Spinal Cord
- Carrying information to and from the brain
- Integration of simple responses
- Reflexes
- Unconscious programmed response to stimuli
42
(No Transcript)
43
The knee-jerk reflex
44
Evolution of Vertebrate Brain
- Evolved from a set of three bulges at the
anterior end of spinal cord - Forebrain (cerebrum)
- Midbrain (optic lobe)
- Hindbrain (cerebellum medulla oblongata)
- Regions have been further subdivided structurally
and functionally
45
Vertebrate Brains
46
Vertebrate Brains
- The relative sizes of different brain regions
have changed as vertebrates evolved - -Forebrain became the dominant feature