Atomic%20Structure PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Atomic%20Structure
1
Atomic Structure
- Atoms are made of 3 subatomic particles
- proton, neutron, electron
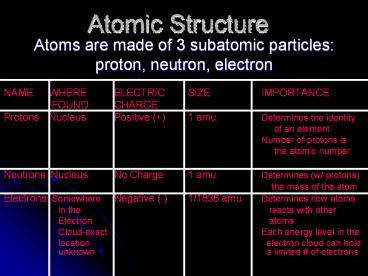
- NAME WHERE ELECTRIC SIZE IMPORTANCE
- FOUND CHARGE
- Protons Nucleus Positive () 1 amu Determines
the identity - of an element
- Number of protons is
- the atomic number
- Neutrons Nucleus No Charge 1 amu Determines (w/
protons) - the mass of the atom
- Electrons Somewhere Negative (-) 1/1836
amu Determines how atoms - in the reacts with other
- Electron atoms
- Cloud-exact Each energy level in the
- location electron cloud can
hold unknown a limited of
electrons
2
Atoms
- AMU Atomic Mass Unit. It is the size of a
proton. It takes 600,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
protons to make 1 gram. - Atoms are electrically neutral. This is because
an atom has the same number of protons (positive
charges) as electrons (negative charges)
3
Chemical Symbol
- An abbreviation that represents the name of an
element - The chemical symbol can contain 1 or 2 letters.
The first letter is always capitalized. The
second letter is lower cased. - Ex.
- Hydrogen H
- Silicon - Si
4
Atomic Number
- Remember Make an A, youre 1!
- Atomic number is the number of protons in an
element. It identifies the element. - If you change the number of protons, you change
the element.
5
Mass Number
- Mass Number- Equal to the number of protons the
number of neutrons in an atom. - MASS NUMBER PROTONS NEUTRONS
- We can use the mass number to find the number of
neutrons an element has. - To find the number of neutrons in an atom,
subtract the atomic number from the mass number. - NEUTRONS MASS NUMBER - ATOMIC NUMBER
6
Atomic Mass
- Atomic Mass The average mass of all known
isotopes of an element. This is found on the
periodic table. - Isotopes are the elements that have atoms with
different numbers of neutrons, so a different
mass number
7
Isotopes
Mass Number
2 1
Chemical Symbol
H
Atomic Number
Ex. Hydrogen Isotopes
1 1
3 1
H H H
2 1
Isotope Name
Protium Deuterium Tritium
(Hydrogen-1) (Hydrogen-2) (Hydrogen-3)
Mass Number
Because the mass number is different for each
isotope of hydrogen, the number of neutrons in
each atom is different. The number of protons,
however, is the same.
8
Reading an element tile on the periodic table
Copy Tile and Labels
Atomic Number (Number of Protons Number of
Electrons)
11 Na Sodium 22.990
Chemical Symbol
Element Name
Atomic Mass (Average Mass of All Known Isotopes)
9
Atoms and APEMAN
- APEMAN A way to remember all parts of an atom
- A Atomic Number
- P Protons
- E Electrons
- M Mass Number
- -A Atomic Number
- N Neutrons
10
Atoms and APEMAN
- Example Sodium-23
- A Atomic Number 11
- P Protons 11
- E Electrons 11
- M Mass Number 23
- -A Atomic Number -11
- N Neutrons 12
11
Copy and Complete the Table Below
Isotope Name Isotope Symbol Atomic Number Mass Number P N E
Iron- 56
16 16 16
K 39
12
Copy and Complete the Table Below
Isotope Name Isotope Symbol Atomic Number Mass Number P N E
Iron- 56 56 Fe 26 26 56 26 30 26
Sulfur- 32 32 S 16 16 32 16 16 16
Potassium- 39 39 K 19 19 39 19 20 19