Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System
Description:
Title: PowerPoint to accompany Author: Karen Benn Marshall Last modified by: sswinehe Created Date: 1/14/2003 11:06:01 PM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:63
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System
1
Chapter 15Cardiovascular System
2
Size of Heart
- Average Size of Heart
- 14 cm long
- 9 cm wide
3
Heart
- Hollow, fist-sized muscular organ
- Located slightly to left of bodys midline
- Acts as dual pumping system
4
Location of Heart
- posterior to sternum
- medial to lungs
- anterior to vertebral column
- base lies beneath 2nd rib
- apex at 5th intercostal space
- lies upon diaphragm
5
Coverings of Heart
6
Pericardium
- Fibrous sac that covers heart
- 2 portions
- Fibrous pericardium-external sac
- Tough, white, fibrous tissue fits loosely around
heart - Protects heart serous membrane
- Serous pericardium internal sac
7
Serous Layer
- Serous layer - a smooth inner sac with lubricated
surfaces which allow movement - parietal layer - lines the inner surface of the
fibrous pericardium - visceral layer - covers the entire surface of the
heart - The potential space between the parietal and
visceral layers of the serous pericardium is the
pericardial cavity.
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
Image courtesy Indigo Instruments. Visit
indigo.com for more original content like this.
12
Heart Wall Layers
- Endocardium
- Myocardium
- Epicardium
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
Wall of the Heart
16
Wall of the Heart
17
Heart Chambers
- Right Atrium
- receives blood from
- inferior vena cava
- superior vena cava
- coronary sinus
- Left Atrium
- receives blood from pulmonary veins
- Right Ventricle
- receives blood from right atrium
- Left Ventricle
- receives blood from left atrium
18
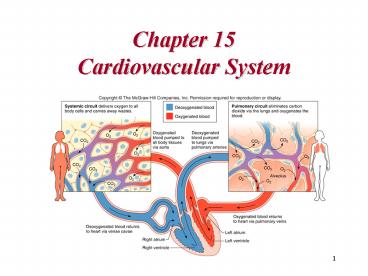
Heart Valves
19
Coronal Sections of Heart
20
Heart Valves
Tricuspid Valve
Pulmonary and Aortic Valve
21
Skeleton of Heart
- fibrous rings to which the heart valves are
attached
22
Path of Blood Through the Heart
23
Path of BloodThrough the Heart
24
Blood Supply to Heart
25
Blood Supply to Heart
26
Angiogram of Coronary Arteries
27
Heart Actions
Atrial Diastole/Ventricular Systole
Atrial Systole/Ventricular Diastole
28
Cardiac Cycle
- Atrial Systole/Ventricular Diastole
- blood flows passively into ventricles
- remaining 30 of blood pushed into ventricles
- A-V valves open/semilunar valves close
- ventricles relaxed
- ventricular pressure increases
29
Cardiac Cycle
- Ventricular Systole/Atrial diastole
- A-V valves close
- chordae tendinae prevent cusps of valves from
bulging too far into atria - atria relaxed
- blood flows into atria
- ventricular pressure increases and opens
semilunar valves - blood flows into pulmonary trunk and aorta
30
Heart Sounds
- Lubb
- first heart sound
- occurs during ventricular systole
- A-V valves closing
- Dupp
- second heart sound
- occurs during ventricular diastole
- pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves closing
Murmur abnormal heart sound
31
Heart Sounds
32
Cardiac Conduction System
33
Cardiac Conduction Control
- Intrinsic internally generated control
- Extrinsic control from outside heart
- Heart rate controlled by both
- A.N.S. can fine tune heart
- S.N.S.-can accelerate heart rate
- P.S.-can slow heart rate
- Hormones-can influence heart rate ex. epinephrine
34
Intrinsic Control
- Sinoatrial node (S.A)
- Atrioventricular Node (A.V.)
- Bundle of His
- Purkinje Fibers
35
Sinoatrial Node
- The natural pacemaker of the heart
- Location - junction of superior vena cava and
right atrium - Impulse for contraction begins at the SA node and
are conducted to the AV node by atrial mycardial
fibers (internodal tracts) - The SA node is supplied by both divisions of the
ANS
36
Atrioventricular Node
- Located in lower right interatrial septum
- Impulse slows
- Slowing allows atria to contract ventricle to
fill with blood
37
(No Transcript)
38
Bundle of His
- Originates in AV. Node
- Divides into left and right branches
- Impulse from AV. Continues into left and right
bundle branches
39
Purkinje Fibers
- Connect bundle branches to lateral walls of
ventricle - Impulse moves through Purkinje fibers reaching
ventricle muscles - Stimulation of ventricle muscles begins in
intraventricular septum moves downward - Depolarization of ventricles contraction
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)
46
(No Transcript)
47
(No Transcript)
48
Cardiac Conduction System
49
Electrocardiogram
- recording of electrical changes that occur in
the myocardium - used to assess hearts ability to conduct
impulses
P wave atrial depolarization QRS wave
ventricular depolarization T wave ventricular
repolarization
50
Electrocardiogram
51
Electrocardiogram
A prolonged QRS complex may result from damage to
the A-V bundle fibers
52
Cardiac Cycle
53
Clinical Application
Arrhythmias
- Ventricular fibrillation
- rapid, uncoordinated depolarization of ventricles
- Tachycardia
- rapid heartbeat
- Atrial flutter
- rapid rate of atrial depolarization
54
Regulation of Cardiac Cycle
Autonomic nerve impulses alter the activities of
the S-A and A-V nodes
55
Regulation of Cardiac Cycle
Additional Factors that Influence HR
- physical exercise
- body temperature
- concentration of various ions
- potassium
- calcium
- parasympathetic impulses decrease heart action
- sympathetic impulses increase heart action
- cardiac center regulates autonomic impulses to
the heart
56
(No Transcript)
57
Blood Vessels
- arteries
- carry blood away from ventricles of heart
- arterioles
- receive blood from arteries
- carry blood to capillaries
- capillaries
- sites of exchange of substances between blood
and body cells - venules
- receive blood from capillaries
- veins
- carry blood toward ventricle of heart
58
Arteries
- Artery
- thick strong wall
- endothelial lining
- middle layer of smooth muscle and elastic tissue
- outer layer of connective tissue
- Carry blood away from heart
- Vascular resistance low
- Mean arterial pressure 100mmHg
59
(No Transcript)
60
Arterioles
- Arterioles
- thinner wall than artery
- endothelial lining
- some smooth muscle tissue
- small amount of connective tissue
- helps control blood flow into a capillary
- Mean pressure 85mmHg
61
Arteriole
- smallest arterioles only have a few smooth
muscle fibers - capillaries lack muscle fibers
62
Venules
- Venule
- thinner wall than arteriole
- less smooth muscle and elastic tissue than
arteriole - Carry blood away from capillaries to veins
- BP 15mmHg when blood returning to heart
63
Veins
- Vein
- thinner wall than artery
- three layers to wall but middle layer is poorly
developed - serves as blood reservoir
- Carry blood from venules to heart
- have valves prevent backflow of blood
- Mean pressure less than 15mmHg
64
(No Transcript)
65
(No Transcript)
66
(No Transcript)
67
Walls of Artery and Vein
68
Capillaries
- smallest diameter blood vessels
- extensions of inner lining of arterioles
- walls are endothelium only single layer
- semipermeable
- sinusoids leaky capillaries
- Join arterioles venules
- Vascular resistance low 35mmHg
69
Capillary Network
70
(No Transcript)
71
Exchange in the Capillaries
- water and other substances leave capillaries
because of net outward pressure at the
capillaries arteriolar ends - water enters capillaries venular ends because
of a net inward pressure - substances move in and out along the length of
the capillaries according to their respective
concentration gradients
72
Venous Valves
73
Characteristics of Blood Vessels
74
Blood Volumes in Vessels
75
Arterial Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure force the blood exerts against
the inner walls of the blood vessels
- Arterial Blood Pressure
- rises when ventricles contract
- falls when ventricles relax
- systolic pressure maximum pressure
- diastolic pressure minimum pressure
76
Pulse
- alternate expanding and recoiling of the
arterial wall that can be felt
77
Factors That InfluenceArterial Blood Pressure
78
Control of Blood Pressure
Controlling cardiac output and peripheral
resistance regulates blood pressure
79
Control of Blood Pressure
If blood pressure rises, baroreceptors initiate
the cardioinhibitory reflex, which lowers the
blood pressure
80
Control of Blood Pressure
Dilating arterioles helps regulate blood pressure
81
Venous Blood Flow
- not a direct result of heart action
- dependent on
- skeletal muscle contraction
- breathing
- venoconstriction
82
Pulmonary Circuit
- consists of vessels that carry blood from the
heart to the lungs and back to the heart
83
Blood Flow Through Alveoli
- cells of alveolar wall are tightly joined
together - the high osmotic pressure of the interstitial
fluid draws water out of them
84
Systemic Circuit
- composed of vessels that lead from the heart to
all body parts (except the lungs) and back to the
heart - includes the aorta and its branches
- includes the system of veins that return blood
to the right atrium
85
Major Vessels of Arterial System
86
Abdominal Aorta and Its Major Branches
87
Arteries to Neck, Head, and Brain
88
Cerebral Arterial Circle
- Circle of Willis
- formed by anterior and posterior cerebral
arteries, which join the internal carotid arteries
89
Arteries to Shoulder and Upper Limb
90
Arteries to the Lower Limb
91
Major Vessels of the Venous System
92
Major Veins of the Brain, Head and Neck
93
Veins from the Upper Limb and Shoulder
94
Veins That Drain the Thoracic Wall
95
Veins That Drain the Abdominal Viscera
96
Veins of the Lower Limb and Pelvis
97
Life-Span Changes
- cholesterol deposition in blood vessels
- heart enlargement
- death of cardiac muscle cells
- increase in fibrous connective tissue of the
heart - increase in adipose tissue of the heart
- increase in blood pressure
- decrease in resting heart rate