Muscle Bone Interaction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Muscle Bone Interaction
Description:
Muscle Movement. When the biceps in the arm contracts the ... ????..??? (biceps), ?? (extensor), ??? (opposing muscles) ????(????????) Muscle Disorders ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:120
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Muscle Bone Interaction
1
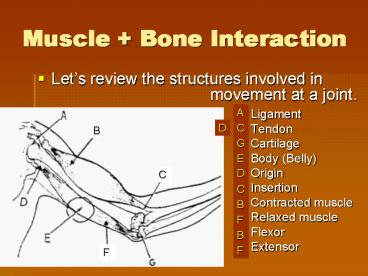
Muscle Bone Interaction
- Lets review the structures involved in
movement at a joint.
A
- Ligament
- Tendon
- Cartilage
- Body (Belly)
- Origin
- Insertion
- Contracted muscle
- Relaxed muscle
- Flexor
- Extensor
D
C
G
E
D
C
B
F
B
F
2
?????????(???,? 11 ?)the extensor in the
movement of the forearm ???????? (biceps), ??
(extensor), ??? (opposing muscles)
????(????????)
3
Muscle Disorders
Sprain
- A sprain is a wrenching, twisting or stretching
injury to a ligament.
- Sprains often affect theankles, knees, or
wrists.
Result in pain, swelling, redness, bruising, and
difficulty using injured joint.
4
Muscle Disorders
Strain
- A strain is an injury to a muscle or tendon, and
is often caused by overuse, force, or stretching.
- Injured area experiences
- pain and soreness
- swelling
- warmth, bruising, or redness
- difficulty using or moving the injured area in a
normal manner
5
Muscle Disorders
Muscle Ruptures
- There are three degrees of muscle ruptures
- A muscle tear may be partial or complete and
caused either by a direct blow or by
overexertion. - A first-degree strain involves less than 5
percent of the muscle. - mild pain and not much loss of strength or range
of motion. - Mild tears referred to as pulled muscles.
- A second-degree tear is a greater rupture that
stops short of a complete tear. - Any contraction of the torn muscle will cause
pain. - There may be a defect of the muscle - a bump or
an indentation - at the site of the most pain. - You should be able to partially contract the
muscle, but not without pain - A third-degree rupture is a complete tear across
the width of the muscle - You will be unable to contract the muscle.
- This is what happens when someone suddenly drops
while sprinting. - The torn end of the muscle may ball up and form a
large lump under the skin, and a great deal of
internal bleeding occurs. - Severely torn muscles may require surgery to heal
properly.
6
Muscle Disorders
Muscle Pull
Muscle Tear
- Muscle pull- very slight tear
- Chronic tear- gradual onset of pain
- Acute tear- sudden dramatic pain
7
Muscle Disorders
Shin splints
- Shin splints is pain resulting from damage to the
muscles along the shin.
Pain is felt in different areas, depending on
which muscles are affected.
Shin splints represent an "overuse injury" and
occur most commonly in runners.
8
Muscle Disorders
Treatment for Muscle Injuries
- R.I.C.E.
- Rest Stop all activities whichcause pain.
- Ice Helps reduce swelling. Never ice more than
10-15 min. at a time. Protect the skin. - Compression Wrap the strained area to reduce
swelling. - Elevation Keep the strained area as close to the
level of the heart as is conveniently possible to
keep blood from pooling in the injured area.
9
Muscle Disorders
Cramps
Spasms
- Muscle spasm- when A muscle (or even a few fibers
of a muscle) involuntarily contract - Muscle cramp- involuntarily forcibly
contracted muscle that does not relax - A forceful sustained spasm
- Nick named charley horse
- Muscle feels tied up in knots
- Can last anywhere from a few seconds to a
quarter of an hour - Caused by strain or injury
10
Muscle Disorders
Tetanus
- Tetanus is a preventable disease through
vaccination - Caused by bacteria that enters the
body through the skin - Found in soil, dust and manure
- Toxin bacteria produces interferes with nerve
transmission to your muscles and causes them to
seize up in painful spasms. - Tetanus typically starts in the jaw and muscles
of the face, quickly spreading to the arms and
legs.
- Lockjaw
- Difficulty swallowing
- Intestines often seize up
- Bladder fails to empty
- Asphyxiation
- Cardiac arrest
11
Muscle Disorders
Anabolic Steroids
- Produced naturally by the body to support such
functions as fighting stress and promoting growth
and development - Referred to as roids, juice, hype, weight
trainers, gym candy, arnolds, stackers, or
pumpers - People use steroid pills, gels, creams, or
injections to improve their sports performance or
the way they look. - Anabolic steroids cause many different types of
problems
- types of problems
- premature balding or hair loss
- dizziness
- mood swings
- problems sleeping
- nausea and vomiting
- high blood pressure
- aching joints
- urinary problems
- shortening of final adult height
- increased risk of heart disease,stroke, and some
cancers
12
Muscle Disorders
Cerebral Palsey
- Cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that
affect a person's ability to move and to maintain
balance and posture.
- The disorders appear in thefirst few years of
life, and usually dont get worse over time. - People with cerebral palsy may have difficulty
walking. They may also have trouble with tasks
such as writing or using scissors. - Some people with cerebral palsy have other
medical conditions, including seizure disorders
or mental impairment. - Cerebral palsy happens when the areas of the
brain that control movement and posture do not
develop correctly or get damaged.
13
Muscle Disorders
Muscular Dystrophy
- Muscular Dystrophy- most well known of hereditary
diseases - A genetic condition that describes over 20
genetic and hereditary muscle diseases. - Characterized by progressive skeletal muscle
weakness, defects in muscle proteins, and the
death of muscle cells and tissue. - In some cases, cardiac and smooth muscles are
affected.
Principal symptoms
- Progressive Muscular Wasting (weakness)
- Poor Balance and Frequent Falls
- Walking Difficulty Waddling Gait
- Limited Range of Movement
- Scoliosis (curvature of the spine)
- Inability to Walk
- Muscle Atrophy and Drooping Eyelids