brain (hypothalamus) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
brain (hypothalamus)
Description:
brain (hypothalamus) pituitary (pituitary level) endocrine ... acromegaly. due to excess GH production. when that GH overproduction begins AFTER adulthood ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:88
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: brain (hypothalamus)
1
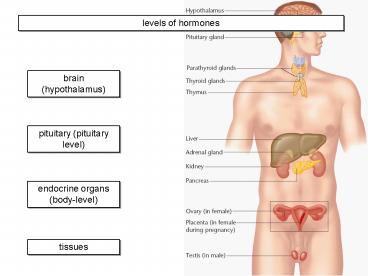
levels of hormones
brain (hypothalamus)
pituitary (pituitary level)
endocrine organs (body-level)
tissues
2
levels of hormones
brain (hypothalamus)
pituitary (pituitary level)
endocrine organs (body-level)
tissues
3
brain (hypothalamus)
pituitary (pituitary level)
endocrine organs (body-level)
tissues
4
brain (hypothalamus)
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Corticotropin-
releasing hormone (CRH) Gonadotropin-releasing
hormone (GnRH) Growth hormone-releasing hormone
(GHRH)
pituitary (pituitary level)
endocrine organs (body-level)
tissues
5
(No Transcript)
6
FSH Follicle-stimulating hormone LH
luteinizing hormone ACTH Adrenocorticotropic
hormone TSH Thyroid-stimulating hormone GH
growth hormone PRL -- prolactin OT --
oxytocin ADH antidiuretic hormone
7
FSH Follicle-stimulating hormone LH
luteinizing hormone ACTH Adrenocorticotropic
hormone TSH Thyroid-stimulating hormone GH
growth hormone PRL prolactin OT --
oxytocin ADH antidiuretic hormone
TROPIC hormones (they activate some other
endocrine gland
have effect on other body tissues (not directly
on other endocrine glands
from the posterior pituitary
8
brain (hypothalamus)
pituitary (pituitary level)
endocrine organs (body-level)
tissues
9
(No Transcript)
10
thyroxin
- thyroid gland releases thyroxin
- thyroxin causes most tissues to increase their
metabolic rate
11
TSH
- to make this happen, ant.pit. releases TSH
thyroid stimulating hormone
12
to make this happen, the hypothalamus releases
TRH
13
what induces the hypothalmus to release TRH?
14
(No Transcript)
15
needed for muscle contraction, fluid balance,
many reactions all over body
needed for strong and resilient bones, joints,
teeth
calcium in bloodstream
calcium in bones
16
needed for muscle contraction, fluid balance,
many reactions all over body
needed for strong and resilient bones, joints,
teeth
calcium in bloodstream
calcium in bones
- too much bone overgrowth, bone spurs
- too little osteoporosis, brittle and fragile
bones
- too much kidney stones, fluid imbalance
- too little weakness, unable to do muscular
actions, shock and possible coma
- skeleton is like a bank
- when more calcium is needed in bloodstream, some
bone is dissolved - this calcium circulates through the bloodstream
- BALANCED against each other
- homeostasis NOT constant!
17
- PTH (parathyroid hormone)
- from parathyroid gland
- in response to low blood Ca2 levels
- (get some Ca2 from the bank)
- calcitonin
- from thyroid gland
- in response to HIGH blood Ca2 levels
- (put some Ca2 IN the bank.)
18
(No Transcript)
19
two very different parts of the adrenal gland
adrenal cortex (outside) secretes cortisol,
aldosterone, other hormones
adrenal medulla (inside) connected directly to
nerve fibers from the hypothalamus secretes
adrenalin and noradrenalin
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
- acromegaly
- due to excess GH production
- when that GH overproduction begins AFTER
adulthood - disproportionate growth of
- skull (mostly jaw)
- fingers hands
- feet toes
- not much in the long bones
26
(No Transcript)
27
exophthalmia protruding eyes hypersecretion of
thyroxine increased pressure on eyes note neck
scar from thyroidectomy
28
- hyperthyroidism
- increased pulse
- excess perspiration
- high BMR
- shortness of breath
- weight loss
- flushed appearance
- exophthalmia
- nervous, anxious, restless
- insomnia
- tremors
29
- Hypothyroidism
- aka myxedema
- if low thyroxin in adult
- low BMR
- lethargy
- dry brittle hair
- impaired memory
- thick tongue
- slow speech
- voice deep and coarese
- diminshished perspiration
- reddened cheeks
- megaloglossia
- increased pigment elbows/knees
30
- usually....
- thyroid makes thyroxine
- when thyroxine level too low, body signals
thyroid gland to make more - but with goiter
- thyroid cant make thyroxine for some reason
- but body is still telling thyroid to make more
- therefore thyroid enlarges
31
(No Transcript)
32
- cretinism
- lack of thyroxine from birth
- or before birth
- could be from lack of thyroid gland
- or lack of iodine in mother
- severe and irreparable mental defects
- stunted growth
- reduced growth and function of many organs
33
(No Transcript)
34
Three different control mechanisms for Hormones
1. feedback inhibition
3. pulsed release
2. releasing/inhibiting
B
A
A
A
A
A
C
B
C
C
C
C
A releases C B inhibits C
A leads to B which leads to C C inhibits
A
A pulses out hormone hormone naturally breaks
down over time then A pulses out more hormone
35
(No Transcript)