Fig. 7-2 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Fig. 7-2
Description:
Title: LE 01-10b Author: System_70 Created Date: 12/12/2005 9:42:59 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) Company: PIT Other titles – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:36
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Fig. 7-2
1
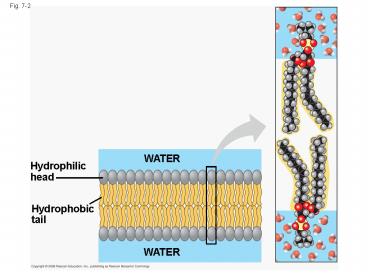
Fig. 7-2
WATER
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tail
WATER
2
Fig. 7-3
Phospholipid bilayer
Hydrophobic regions of protein
Hydrophilic regions of protein
3
Fig. 7-7
Fibers of extracellular matrix (ECM)
Carbohydrate
Glyco- protein
Glycolipid
EXTRACELLULAR SIDE OF MEMBRANE
Cholesterol
Microfilaments of cytoskeleton
Peripheral proteins
Integral protein
CYTOPLASMIC SIDE OF MEMBRANE
4
Fig. 7-9
Signaling molecule
Enzymes
Receptor
ATP
Signal transduction
(a) Transport
(b) Enzymatic activity
(c) Signal transduction
Glyco- protein
(d) Cell-cell recognition
(e) Intercellular joining
(f) Attachment to the cytoskeleton and
extracellular matrix (ECM)
5
Fig. 7-7
Fibers of extracellular matrix (ECM)
Carbohydrate
Glyco- protein
Glycolipid
EXTRACELLULAR SIDE OF MEMBRANE
Cholesterol
Microfilaments of cytoskeleton
Peripheral proteins
Integral protein
CYTOPLASMIC SIDE OF MEMBRANE
6
Fig. 7-5
Lateral movement (107 times per second)
Flip-flop ( once per month)
(a) Movement of phospholipids
Fluid
Viscous
Unsaturated hydrocarbon tails with kinks
Saturated hydro- carbon tails
(b) Membrane fluidity
Cholesterol
(c) Cholesterol within the animal cell membrane
7
Fig. 7-7
Fibers of extracellular matrix (ECM)
Carbohydrate
Glyco- protein
Glycolipid
EXTRACELLULAR SIDE OF MEMBRANE
Cholesterol
Microfilaments of cytoskeleton
Peripheral proteins
Integral protein
CYTOPLASMIC SIDE OF MEMBRANE
8
Fig. 7-11
Molecules of dye
Membrane (cross section)
WATER
Equilibrium
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
(a) Diffusion of one solute
Equilibrium
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Equilibrium
(b) Diffusion of two solutes
9
Fig. 7-17
Passive transport
Active transport
ATP
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
10
Fig. 7-11
Molecules of dye
Membrane (cross section)
WATER
Equilibrium
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
(a) Diffusion of one solute
Equilibrium
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Equilibrium
(b) Diffusion of two solutes
11
Fig. 7-12
Higher concentration of sugar
Lower concentration of solute (sugar)
Same concentration of sugar
H2O
Selectively permeable membrane
Osmosis
12
Fig. 7-13
Hypotonic solution
Isotonic solution
Hypertonic solution
H2O
H2O
H2O
H2O
(a) Animal cell
Lysed
Normal
Shriveled
H2O
H2O
H2O
H2O
(b) Plant cell
Turgid (normal)
Flaccid
Plasmolyzed
13
Fig. 7-UN1
Passive transport Facilitated diffusion
Channel protein
Carrier protein
14
Fig. 7-UN2
Active transport
ATP
15
Fig. 7-16-7
EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
Na
Na high
Na
K low
Na
Na
Na
Na
Na
Na
ATP
Na low
P
Na
P
K high
CYTOPLASM
ADP
2
3
1
K
K
K
K
K
P
K
P
6
5
4
16
Fig. 7-20a
PHAGOCYTOSIS
CYTOPLASM
EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
1 µm
Pseudopodium
Pseudopodium of amoeba
Food or other particle
Bacterium
Food vacuole
Food vacuole
An amoeba engulfing a bacterium via phagocytosis
(TEM)
17
Fig. 7-20b
PINOCYTOSIS
0.5 µm
Plasma membrane
Pinocytosis vesicles forming (arrows) in a cell
lining a small blood vessel (TEM)
Vesicle
18
Fig. 7-20a
PHAGOCYTOSIS
CYTOPLASM
EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
1 µm
Pseudopodium
Pseudopodium of amoeba
Food or other particle
Bacterium
Food vacuole
Food vacuole
An amoeba engulfing a bacterium via phagocytosis
(TEM)
19
Fig. 7-10
ER
1
Transmembrane glycoproteins
Secretory protein
Glycolipid
2
Golgi apparatus
Vesicle
3
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasmic face
4
Extracellular face
Transmembrane glycoprotein
Secreted protein
Membrane glycolipid