Carbon compounds The chemistry of life - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title: Carbon compounds The chemistry of life
1
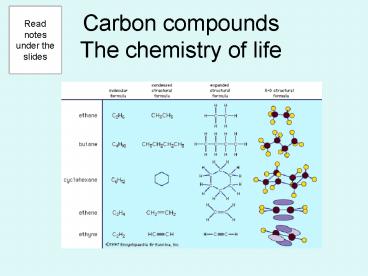
Carbon compoundsThe chemistry of life
Read notes under the slides
2
Organic molecules
- Organic molecules all contain carbon.
- Usually bonded to N, H, O, P, S.
- CHNOPS most common 6 elements in organisms.
Amino acid alanine
3
Why Carbon
- Carbon forms the backbone of the molecule.
- Carbon bonds with 1,2, 3, or 4 covalent bonds.
- Macromolecules are made up of chains of monomers.
- Functional groups give characteristics to the
molecule
Single bonds
Triple bonds
Double bonds
Think what is an analogy for the relationship
between monomers and macromolecules?
4
macromolecules
- Organisms are made of many types of molecules.
- There are 4 types of macromolecules that are most
important to the running of cells. - Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Nucleic Acid
5
Condensation reactions
- Condensation (dehydration) reactions link
monomers into polymers. - Hydrolysis breaks polymers into building blocks
(monomers).
Think why is water needed to break these bonds
but not to form them?
6
Monosaccharides
- Saccharides are simple sugars
- Glucose C6H12O6.
- 2 linked form disaccharides.
- Ex lactose, sucrose, maltose.
- Sugars usually have names that end in ose
Glucose
7
Carbohydrates
- Composed of monosaccharides.
- Only C,H,O.
- Hydrogen to oxygen ratio is 21.
- Used for structure and energy storage.
- Most common polysaccharides
- Starch
- Cellulose which is the most common carbohydrate
Plant Cell Walls
8
Amino acids
- Carbon atom
- Amino group
- R group (radical)
- Hydrogen
9
polypeptide
- Dipeptide is a molecule composed of two amino
acids. - Connected by a covalent bond called a peptide
bond. - Many amino acids hooked together are called a
polypeptide.
Four polypeptides of hemoglobin
10
Proteins
- A protein is a polymer of amino acids.
- 20 different types of amino acids found in
nature. - Proteins are either for structure or enzymes.
- Composed of C,H,N,O.
A large protein such as an enzyme
11
Lipids
- Lipids are fats
- They are made of fatty acids and glycerol
- Lipids are nonpolar which makes them
hydrophobic which means they dont mix with
water - Fats, oils, and wax are all lipids
12
Nucleic Acids
- Nucleotides are the monomers that make up nucleic
acids - They contain 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group,
and nitrogenous base - DNA and RNA are important nucleic acids
13
Summary questions (answer in paragraph form)
- Name each macromolecule and the monomers that
form them. - What do functional groups do?
- Why is carbon important?
- What are the 5 other elements found in
macromolecules?