Crenate PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Crenated cell. Tear drop cell. Sickle cell ... crenated cell. hypochromic. hyperchromic. normochromic. polychromatophilic. macrocytic/normochromic ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Intracellular cations = Intracellular anions (mEq/L) ... primary active transport (active, uses ATP) ... Crenated red cells. 26. Osmolarity and tonicity ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Basic unit of structure & function in body. Highly organized molecular factory ... crenated. 6-19. Regulation of Blood Osmolality ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Boiling Point Elevation. Osmotic Pressure. Osmosis and Dialysis. Osmosis. Osmotic membrane ... Boiling Point Elevation. Candy making. Crenation. Pickles ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
products prepared in environmentally controlled areas ... causes cells to crenate or shrink. hypotonic = lower P than cells. causes cells to rupture (lyse) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Insufficient or excess anticoa. -Inadequate mixing of blood with ... vacuolisation & irregular lobulation of nucleos -crenation &sphering of RBC(after 6 hours) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Includes all constituents of body outside cells. 67% of total body H20 is inside cells (=intracellular ... crenated. 6-19. 32. Transport by Carrier Proteins ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
There is movement in both directions across a semipermeable ... Crenation of Red Blood Cells, Electron Micrograph. Colligative Properties. Osmosis. Hemolysis: ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
transports particles against their concentration gradient ... cells in this solution would lose water shrivel (crenate) Isotonic solution = normal saline ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Several lesions may coalesce and epithelial filaments are present ... Lesions coalesce and spread in all directions to form large shallow ulcer with crenated edges. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
3 wk : formation of blood islands from yolk sac. 6 wk : liver becomes ... (crenated cells, burr cells) regularly contracted cells with smooth surface undulation ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
the membrane is a mosaic of numerous protein molecules (mlc) bobbing in a fluid ... crenate. hypotonic soln: ( 0.85% NaCl) hemolyze. 23. Osmosis cont. osmoregulation ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
1. centrifuged whole blood results in erythrocytes at bottom, serum at top, and ... (note crenated rbcs usually caused by preparation methods) V. Leukocytes ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
We will look at the movement of two dyes as they diffuse through an ... Crenate (spiky, not smooth edge) Photo: Jeff Beck, CCCCD. RBCs in hypotonic solution ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
all organisms are made of cells. All cells rise from preexisting cells ... hypertonic - net loss of water by cells (crenate) hypotonic - net gain of water by cells ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Isotonic solutions: if the osmotic concentrations of both solutions are equal than no net movement of water occurs Examples include most interstitial fluid and most ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Movement of Substances BINGO Write any 12 into your grid turgor pressure cohesion / cohesive diffusion osmotic pressure (fully) permeable active concentration ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to ... Turgid cell- plant cells that maintain a good osmolarity & tonicity- appear round & happy! ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chondrocytes / Hyaline Cartilage Transitional epithelium Reticular Tissue Fibrocartilage Cardiac muscle Simple Cuboidal Bone tissue Bone tissue close-up Hyaline ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Moving through the Plasma Membrane Environment outside cell Water moves Effect on ANIMAL cell Effect on PLANT cell Hypotonic In Swells, then bursts (cytolysis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
LEAF MORPHOLOGY leaf sheath Dicotyledonous leaf Monocotyledonous leaf leaf apex leaf margin blade/lamina leaf vein petiole stipule ligule auricle abscission zone ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Slug. Importance in plants and animals. turgor pressure. OSMOSIS IN EVERYDAY LIFE ... Salt on a slug. Contractile vacuoles in plants. Saltwater and Freshwater fish ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: No Slide Title Author: Simon & Schuster Last modified by: Jeffrey Venables Created Date: 2/20/2002 4:52:36 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Membranes The Cell Membrane Cell Membrane: Phospholipid Molecule Model Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Every cell is encircled by a membrane and most cells ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: C H E M I S T R Y Subject: CHEMISTRY and BRANCHES Author: ASKEW Last modified by: Carolyn Ragland Created Date: 6/19/1996 11:38:00 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Transport across the plasma membrane Structure of the plasma membrane This diagram shows the currently accepted fluid mosaic model for the membrane structure.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
movement of substances down a concentration gradient (from high to low) ... organisms living in freshwater use contractile vacuoles to pump excess water out ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Phospholipid bilayer--two layers of phospholipid sheets. Phospholipids polar head --hydrophilic (water loving) non-polar--hydrophobic tail ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Sideroblast (nucleus stains red, iron pigment stains blue) ... (white tailed deer) Theileria sp. drepanocytes. 58. Hemoparasites (Plasmodium or Hemoproteus) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... on the same day, post mortem examination showed massive intraventricular ... (post mortem) AML-M3 / Promyelocytic Leuk. 10% of AML are Promyelocytic (M3) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Solute. Solvent. Dilute vs. concentrated. Miscible/immiscible. Solubility. Saturated; unsaturated ' ... Id solute. Id solvent. Temperature. Concentration ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Diffusion Through a Membrane When Placed in a Hypotonic Solution In plant cells, the central vacuoles (large storage areas) will fill and the plant becomes stiff and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Membrane & Cellular Transport
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Leaf Identification to identify broad and narrow shaped leaves to identify simple and compound leaf groupings to identify leaf arrangement to identify leaf margin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Movement of molecules from high concentration to low ... Turgid. hypotonic solution. water enters cell. chloroplasts are at the periphery of the cell ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
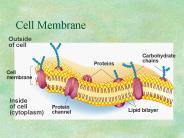
Cell Membrane Outside of cell Carbohydrate chains Proteins Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell Membrane Outside of cell Carbohydrate chains Proteins Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis LEQ: How does passive transport move chemicals across a cell membrane? Reading: 3.5, 3.2 (focus on organelles with membranes)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
CELLS Basic unit of life Cell theory Cytology study of cells Accomplished by LM, SEM, TEM CELL MEMBRANE Selectively permeable Physical isolation Regulation of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
PPM,PPB,Molarity ,Molality.Mole Fraction etc
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Erythrocytes aka RBC s Laboratory Procedures Acanthocytes (Spur Cells) The term acanthocyte is derived from the Greek word acanthi meaning thorn ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The concentration of solute in the solution can be equal to the concentration of ... Movement of substances against a concentration gradient. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: SHA Last modified by: Henry, Kidane Created Date: 11/14/2006 12:15:23 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Diffusion and Osmosis Intermediate 2 Diffusion Osmosis Definition of Osmosis Osmosis is the movement of water molecules, from a region of high water concentration to ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Roots, Stems, and Leaves
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Erythrocytes aka RBC s Laboratory Procedures Drepanocytes Keratocyte (Helmet Cells) Also called blister cells or bite cells. Keratocytes are associated with trauma ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Cell Membrane
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
URINE ANALYSIS Macroscopic urinalysis Is the direct visual observation of the urine, noting its volume, color, clarity or cloudiness, etc Normal urine is typically ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Dynamics Human Anatomy and Physiology II Oklahoma City Community College Dennis Anderson * Which way will water move in this example?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... is studying in the same room, gradually begin to smell the scent of the perfume... Drop a piece of copper sulphate crystal into a gas jar full of water. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Membrane Structure and Function Topic 3 Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Amphipathic liquid-crystal properties/behavior allow for constant movement of HC ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Diffusion and Osmosis Outline Learn the concepts of: Diffusion, osmosis, semi-permeable membrane, isotonic, hypertonic, & hypotonic Explore diffusion in a colloid ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell Membranes and Transport B9 - Analyze the structure and function of the cell membrane Cell Walls NB** Cell walls are different from cell membranes Stiff, non ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chang Gung University Department of Medical Biotechnology Clinical Hematology Biology of the Red Cell IV & V Membrane and other cytoplasmic components
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Transport Flip n Go
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
VARIATION IN SIZE OF THE RBC. GRADING OF MICROCYTOSIS. 1 5 TO 20% OF RBCs PER OIF ARE MICROCYTIC ... BURR CELLS. STOMATOCYTES. GRADING OF POIKILOCYTOSIS ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view