Prentice Hall Biology PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Prentice Hall Biology
1
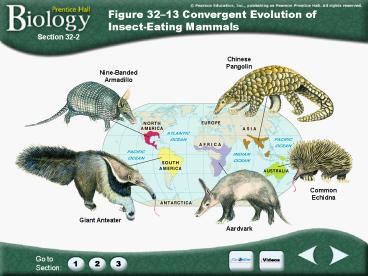
Figure 3213 Convergent Evolution of
Insect-Eating Mammals
Section 32-2
ChinesePangolin
Nine-BandedArmadillo
CommonEchidna
Giant Anteater
Aardvark
2
Interest Grabber
Section 32-3
- Skeletal Features of Primates
- Recall that primates are an order of mammals. One
difference that exists between primates and other
mammals is in the structure of the primate
skeleton. Some examples of primates include
humans, lemurs, monkeys, and apes.
1. How are the external features of your hands
different from the external features of the paws
of a dog or the hooves of a horse? 2. Primates
are bipedal, or capable of walking on two limbs.
What is an advantage of being bipedal? 3. What
are some characteristics of your skeleton that
enable you to stand and walk?
3
Comparison of Skulls of Human Ancestors
Section 32-3
Large brow ridge
Large nose
Large canine teeth
Face protrudes forward
Australopithecus afarensis
Homo erectus
Round, high skull
Weak brow ridge
Large brain case
Inflated cheeks
Largenose
Even teeth
Strong chin
Neanderthal
Cro-Magnon
Modern Homo sapiens
4
Figure 3216 Human and Gorilla Skeletons
Section 32-3
Comparing Human and Gorilla Skeletons
Modern Human
Modern Human
Modern Gorilla
Modern Gorilla
Skull atopS-shaped spine Spinal cord exitsat
bottom of skull Arms shorter thanlegs hands do
not touch groundduring walking Pelvis is
bowl-shaped Thigh bones angledinward,
directlybelow body
Skull atopC-shaped spine Spinal cord exitsnear
back of skull Arms longer thanlegs hands touch
ground during walking Pelvis is longand
narrow Thigh bones angledaway from pelvis
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.