PowerPoint-Pr - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
PowerPoint-Pr
Description:
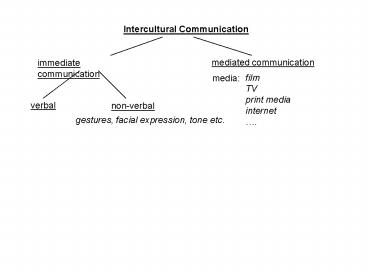
Intercultural Communication mediated communication immediate communication film TV print media internet . media: verbal non-verbal gestures, facial expression ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:43
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PowerPoint-Pr
1
Intercultural Communication
mediated communication
immediate communication
film TV print media internet .
media
verbal
non-verbal
gestures, facial expression, tone etc.
2
Intercultural competence
behavioural competence
communicative competence (verbal, non-verbal)
comprehensive competence
understanding and interpretation of symbols and
signs
? everyday rituals
? dress codes
? literature
?
cognitive dimension
affective dimension
knowledge about cultural values and communication
styles, e.g. also specific knowledge in business
contexts
ability to develop an understanding for
foreign cultures and to deal sensitively with
strange/unknown things whose reasons and
backgrounds we don't understand.
3
Intercultural communication pitfalls
(Wahrnehmungsfallen)
1. different meanings of words/terms
2. divergence conventions of speech ? intention
3. communication styles
4. topics
5. register/tone
6. paraverbal factors
7. non-verbal factors
8. specific cultural standards
9. specific cultural conventions
4
1. Different meanings of words/terms
e.g. frz. "famille" ? extended family, relatives
"nation" ? in different cultures with positive or
negative connotations
2. Divergence conventions of speech ? intention
acceptance/refusal is often not expressed clearly
e.g. ? invitation in France "Est-ce que je
peux vous inviter à déjeuner demain?"
convention "Oui, si vous voulez."
? sounds non-obligatory (unverbindlich)
? correct meaning "Yes, thank you!"
? business negotiations in Asia
statement of the Asian partner "I'll do the best
I can ."
? correct meaning break-off of negotiations
without any solution
5
3. Communication styles
greeting rituals, turn-taking (pausing/overlapping
), small talk/"deep talk", direct/indirect
e.g. ? greeting rituals
? in European cultures relatively little time
devoted to greetings African cultures daily
greeting ritual includes enquiring after
well-being, also the well-being of family
members
? France etc. Wangenkuss
? Japan highly codified bowing
? turn-taking
pausing (silence) between turns
? overlapping (start before the other
finishes)
?
?
can mean different things in different cultures
can mean different things in different cultures
- respect
- indication of respect
Asia Finland
- cooperation
- cooperation
- lack of interest
- aggressiveness
- shyness
- rudeness
Europe USA
- embarrassment
- passive aggressiveness
6
? Small talk ? deep talk
German
American
Objective?
e.g. "I have a grandmother in Germany!"
Deep talk Serious discussion
Small-talk
Objective
Objective
Building up relationship, finding commonalities
Kennenlernen "Tiefe" Sachlichkeit
"Testing the waters"
Different opinions are also ok
Friendliness
Americans don't contradict in this phase of
conversation. Instead they are just quiet or say
something like "That's interesting!"
Wavelength
"Germans are too serious, demanding, arrogant!"
"Americans are superficial"
Stereotypes
7
? direct ? indirect
? degree of directness in which statements are
made
refers especially to
- requests
? typical British request if music is too loud
"I think the walls are rather thin here"
- expression of individual opinions/attitudes
- apologizing (Asian countries ? fear of loss of
face)
direct German way to express criticism, to
contradict etc. is not appreciated everywhere
? see also Hall high context vs. low context
8
4. topics
e.g. ? Japan topics concerning 'money',
'taste', 'personality', 'body' are avoided
? Frankreich - no advertising for tampons or
certain other medical products
- conversational topics politics, scandals
? Spain/Italy football, family matters
? Turkey family, job, football avoid politics
5. register/tone (richtiger Ton)
e.g. humor/irony/sarcasm
? often used to find an additional common level
of understanding but may often be
misinterpreted
9
6. paraverbal factors
? loudness, intonation, pitch, tone, rhythm,
tempo etc.
e.g. - Asian intonation falls with polite
questions
? European interpretationimpolite
- German loudness is mostly considered
impolite/rude
7. non-verbal factors
gestures, facial expressions, eye contact,
etiquette, dress codes etc.
8. additional/specific cultural standards and
attitudes in certain cultures
- France sense of honour, solidarity,
rationalism (believe in progress/technology)
- China Confucian principles (strict hierarchy,
group harmony, politeness, strong work ethic)
9. other specific cultural conventions
- Britain staring at other people is rude
e.g.
- GB/USA first names also for superiors
? danger may be misinterpreted